Iliopsoas, пояснично-подвздошная мышца - техники расслабления и укрепления
Для основ: где расположена и какое действие производит см. Мышцы таза http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24852.html, не вижу смысла переносить сюда, слишком большой объём.
http://www.emedicine.com/sports/TOPIC52.HTM
Acute injury and overuse injury are the 2 main causes of iliopsoas tendinitis. The acute injury typically involves an eccentric contraction of the iliopsoas muscle, but also may be due to direct trauma. Overuse injury may occur in activities involving repeated hip flexion or external rotation of the thigh. Activities that may predispose to iliopsoas tendinitis include dancing, ballet, resistance training, rowing, running (particularly uphill), track and field, soccer, and gymnastics.
During the adolescent growth spurt, the hip flexors tend to become relatively inflexible. This inflexibility can lead to problems in younger athletes because stress placed on the iliopsoas musculotendinous unit increases and general biomechanics are altered. Tightness of the iliopsoas, tensor fascia lata, or rectus femoris can lead to inhibition of the gluteus maximus, allowing for an anterior pelvic tilt. This in turn leads to adverse affects on the kinetic chain. Excessive anterior tilt can lead to increased lumbar lordosis with resultant stress on the lower lumbar discs, facet joints, and sacroiliac joints and may result in increased knee flexion at heel strike and during midstance phases of the gait cycle. The subsequent increase in eccentric load across the knee extensor mechanism may result in patellar tendon injuries. With increased knee flexion, compressive forces at the patellofemoral contact surface increase and may predispose to patellofemoral problems.
Перевод francuz_bel, коррекция моя.
Острая травма и травма переиспользования являются двумя основными причинами тендинита (Тенденит (tendinitis) - воспаление сухожилия). Острая травма обычно является следствием необычного сокращения подвздошно-поясничной мышцы, но также может случиться по причине прямой травмы. Травма переиспользования может случиться в результате действий, включающих в себя повторяющиеся сгибания бёдер или разворот бёдер наружу. Действия, располашающие к тендиниту: танцы, балет, тренировки сопротивлению, гребля, бег (особенно в гору), лёгкая атлетика, футбол и гимнастика.
Во время подросткового скачка роста сгибатели бедра имеют тенденцию к потере гибкости. Эта потеря гибкости может привести к проблемам у молодых атлетов, т.к. нагрузка оказываемая на подвздошно-поясничную мускулатуру, возрастает и общая биомеханика меняется. Напряжение пояснично-подвздошной мышцы, напрягателя широкой фасции бедра, или прямой мышцы бедра может привести к угнетению ягодичной мышцы, приводя к наклону таза вперёд. Это, в свою очередь, приводит к неблагоприятным эффектам кинетической цепочки. Чрезмерный наклон вперёд может приводить к усиленному поясничному лордозу с проистекающим давлением на нижние поясничные диски, суставы и крестцово-подвздошные суставы и может приводить к увеличению сгибания коленей в момент удара пятки о землю и в средгий момент цикла шага. Последующее усиление необычной нагрузки на коленный разгибательный механизм может привести к повреждениям надколенного сухожилия. С усилением сгибания колена компрессионные силы в месте соединения прямой мышцы бедра с надколенным сухожилием возрастают, что предрасполагает проблемам в этом месте.
Всё это входит в прямое притиворечие с информацией отсюда http://zakazdiplom.ru/show_work.php?work=12033 или http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/28307.html
Этот метод лечения способствует уменьшению наклона поясничного отдела позвоночника на стороне тренировки пояснично-подвздошной мышцы.
http://blog.360.yahoo.com/blog-yQEIEIs8er7tz9YyK.Ak2NxAs1XJ
In the 1950’s Lawrence Jones, D.O. discovered by accident that when he placed the body into a comfortable position pain and dysfunction would heal quickly. He initially called this approach to pain “spontaneous release by positioning.” This work is now known generically as Positional Release or as the "fold and hold" technique." In most cases the position created is the original position of injury or an abnormal bony relationship. NRT is a variation of positional release that has been developed for use by Massage professionals.
http://www.naturalreflexes.com/pages/Psoas.html
http://www.squidoo.com/psoas
Understanding and Releasing the Psoas Muscle
Понятие и освобождение поясничной мышцы
What keeps the psoas in contraction?
The psoas will stay contracted because of postural habits and trauma. The way we stand, walk and sit can distort the it. If we walk or stand with our chin in an overly forward position the muscle will tighten. Ida Rolf wrote, "a deteriorated psoas" chronically flexes the body at the level of the groin, so that it prevents truly erect posture.?7 Sitting through much of the day the psoas shortens to keep us bio mechanically balanced in our chairs. Over time we develop a "normal" way of holding the psoas that is dysfunctional.
Unresolved trauma can keep the psoas short and reactive. After a traumatic occurrence animals will release their protective responses by shaking. Humans often bypass this release response and hold the trauma in their bodies.8 Until the psoas is released the muscle may stay contracted and fearful and go into further shortening and spasm very easily.
Что держит поясничную мышцу сокращенной?
Поясничная мышца остается сокращенной (стянутой) в результате пагубного воздействия неправильной осанки или травмы. То, как мы стоим, идет или сидим могут ухудшать состояние поясничной мышцы. Если мы ходим или стоим с чрезмерно выпяченным вперед подбородком, то мышца будет сокращаться. Ида Рольф написала “истощенная поясничная мышца” хронически изгибает тело на уровне паховой области так, что это препятствует по-настоящему полному выпрямлению осанки. Долгое сидение на протяжении дня сокращает поясничную мышцу чтобы поддерживать нас в биомеханическом балансе на наших стульях. Через какое-то время мы создаем “нормальный”, “обычный” стереотип держания мышцы, который не является правильным.
Непролеченная до конца травма может держать мышцу сокращенной. Животные после травматического эпизода снимают результаты действия защитного инстинкта встряхиванием. Люди часто обходят эти инстинкты и держат последствия травмы в своем теле. Пока поясничная мышца не расслаблена, она может оставаться сокращенной и напряженной, и дальше легко спазмироваться и укорачиваться.
Releasing the Psoas Muscle with Natural Reflex Therapy
How does Natural Reflex Therapy release the psoas?
NRT creates a comfortable position for the psoas that typically shortens the muscle. Through fine tuning and client feedback the best position is discovered. Within seconds the body may begin to release spasm, restore normal muscle tone, increase circulation, remove pressure on nerves, and allow bones and joints to move freely. Often, by recreating the original strain the muscle is restored to a normal range of contraction and relaxation.9 To keep the psoas in its normal range, we must also place the pelvis and spine into positions that restore optimum biomechanical function. All the energy and attention that was used to deal with pain is now available to the body's healing process.
These positions stimulate specific reflexes in the body that help to restore a better balance to the psoas, pelvis and lumbar vertebrae. The reflexes that we stimulate are found within the proprioceptive nervous system, which monitors and helps coordinate all muscular movements. These reflexes give us our sense of our shape, density, quality and speed of movement, and effort. .
Because this method is indirect there is less chance of re-traumatizing the muscle or stimulating new spasm. Rather than trying to force the muscle to change, the reflexes that hold the psoas in contraction are allowed to reset a new state of structure and function. When the reflexes learn/remember how to restore balance there is a greater chance of long lasting or permanent changes. When the psoas has freedom of movement and function, the client is encouraged to use movements and exercises that will prevent future occurrences.
Over time the client can learn to maintain and control the psoas, that hidden prankster, and its role in the essential balance of our core structures. Referred pain patterns are discontinued when the seat of the disturbance is relieved. The client can begin to remember the sense or feeling of a dynamically neutral orientation as comfort. With specific exercise and better posture they can keep the psoas from shortening. Conditions recover and the possibility of elegance is made more possible. Our capacity to protect ourselves, without holding trauma, improves, particularly when other forms of therapy are added to the process. With renewed structural integrity, enhanced circulation, unimpinged nerve function, and flowing chi we are sustained at a higher level of health.
Лечение пояснично-подвздошной мышцы методом натуральной рефлексотерапии (НРТ)
Как это возможно?
НРТ создает комфортные условия для мышцы, которая обычно сокращена. С помощью качественной настройки и обратной связи с клиентом находится наилучшая позиция. В течении нескольких секунд тело может начать справляться со спазмом, восстанавливать нормальный мышечный тонус, усиливать циркуляцию крови, избавляться от нервного напряжения, и позволять костям и суставам двигаться свободнее. Часто мышца возвращется в нормальный режим сокращения и напряжения путём воспроизводства первоначального напряжения. Чтобы поддерживаться мышцу в нормальном тонусе мы должны также распологать таз и спину в положения, которые обеспечивают оптимальное выполнение биомеханических функций. Вся энергия и внимание, которые были использованы в борьбе с болью сейчас имеются в наличии для того чтобы запустить излечивающие силы организма.
Такие положения стимулируют специфические рефлексы в организме которые помогают восстановить лучший баланс мышцы, таза и поясничных позвонков. Рефлексы, которые мы стимулируем, основаны на проприоцептивной нервной системе, которая наблюдает и помогает координировать все движения мышц. Эти рефлексы дают нам чувство нашего тела, плотности, качества и скорости движения и усилий.
Проприоцептор - рецепторы, которые находятся в основном в мышцах, связках, суставах, и во внутреннем ухе, определяют движение или положение тела или конечности, отвечая на стимулы, происходящие внетри организма.
Т.к. этот метод непрямой, то получается меньше шансов еще раз травмировать мышцы или стимулировать новый спазм. Лучше чем пытаться форсировать изменение мышц, ма позволяем рефлексам, которые удерживают поясничную мышцу в напряжении, установить новое положение скелета и функций. Когда мы изучаем или вспоминаем как восстановить баланс на уровле рефлексов, появляется наилучший шанс длительных или постоянных изменений. Когда поясница свободна в движениях и функционирует нормально, клиент поддерживает движения и упражнения, которые предупреждают будущие происшествия.
Через какое-то время клиент может научиться поддерживать и контролировать поясничную мышцу, этого скрытого шутника, и ее роль в балансе нашей ключевой структуры. Вышеупомянутые болевые паттерны прекращаются когда место возбуждения расслабляется. Клиент может начать вспомнать чувство или ощущение динамически нейтрального положения как комфорт. С помощью специальных упражнений и хорошей осанки они могут уберечь поясничную мышцу от спазмирования. Эти условия возвращают и возможность грации в движениях. Наша способность защищать себя, отпуская травму, улучается особенно тогда когда другие формы терапии добавлены к процессу. С обновленной целостностью структуры, улучшенной циркуляцией, освобождённой от ущемлений нервной функцией и большим количеством энергии мы поддерживаемся на высочайшем уровне здоровья.
http://www.menshealth.com/cda/article.do?site=MensHealth&channel=fitness&category=sports.injuries&conitem=294144debb8a3010VgnVCM100000cfe793cd____
What is the cause of Lordosis?
Some muscles around the hip and spine become tight and some become weak and stretched, causing an imbalance. The muscles that are often tight are:
Trunk extensors (erector spinae and quadratus lumborum).
Hip flexors (in particular the iliopsoas muscle).
These muscles require stretching.
The muscles that are often weak and stretched are:
Abdominal muscles (rectus abdominus, internal oblique and external oblique)
Hip extensors (hamstrings and gluteus maximus).
These muscles require strengthening.
Что является причиной лордоза
Некоторые мышцы бедра и спины сжимаются, а некоторые становятся слабыми и растянутыми, что ведёт к дисбалансу.
Мышцы, которые часто сжимаются: разгибатели корпуса (erector spinae и quadratus lumborum, http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24805.html) и сгибатели бедра, в частности, подвздошно-поясничная мышца, http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24852.html. Этим мышцам часто требуется растяжка.
Мышцы, которые часто слабы и растянуты: мышцы живота (rectus abdominus, internal oblique и external oblique, http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/26243.html) и разгибатели бедра (hamstrings (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris, http://www.anatomix.ru/anat/anat211.htm и gluteus maximus http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24852.html). Эти мышцы нуждаются в укреплении.
http://www.scoliosis.org/forum/archive/index.php/t-179.html
I'm a bodyworker specializing in postural and orthopedic concerns, and I frequently work with the psoas muscle. There is a definite correlation between the psoas and scoliosis.
A chronically tight psoas will wreak havoc with the lower spine. When the upper fibers of the psoas are tight, it tends to put the spine into hypo-lordosis (decreases the natural curve of the lower spine.) When the lower fibers of the psoas are tight, it tends to place the lumbar spine into hyperlordosis (an increase of that curve.) Frequently, in scoliosis, one side is tighter than the other, or one side is tight on top and the other side tight on the bottom. This will lead to a torquing effect of the lumbar spine and pelvic girdle.
There is a way to access the psoas yourself, but please be careful. I've never met you, and I'm not sure if there would be any contraindications in your case. Anything wrong in the abdomen, like intensinal problems would be a contraindiacation. Basically, you take an inflatable ball just a little larger than a tennis ball, place it on the floor, and lay on it. You'll be face-down, and the ball will be just to the side of your belly button. Ease your weight down on it until you feel an area of tension or a hot, crampy sensation. You would continue to ease your weight down on it as the psoas loosens up. Then you would move the ball out and down a bit. Any time you find tension or the hot-crampy sensation, allow your body weight to gently ease down onto the ball as the tension releases. Do both sides.
I've seen balls the proper size at Walmart in their huge bins and also at pet stores as dog toys. Some school supply places carry them. You're looking for something with about a 4" diameter. If you're very small framed, you might go a little smaller, or if you're very large, then maybe something slightly larger. But so far, with most of my clients, the 4" ball seems to work very well.
Another good way to get the psoas to release some tension is to trigger it to do so indirectly. Muscles work in pairs. To move any joint, one muscle has to contract while another relaxes. If you contract the muscles opposite the psoas, it will trigger the psoas to relax some. (As you follow these directions, if anything feels wrong to your body, please discontinue. As I've said, I've never met you, and I don't know what particular contraindications might apply in your case.) You'd lie on your back with knees bent. Bring one knee toward your chest and clasp your hands behind your knee. Try to push your foot back toward the floor while your arms are trying to pull that leg closer to your chest. You're contracting your hamstrings, which are the main hip extensors. Hold the tension for about 10 seconds and then switch sides. Repeat so that you've done each side about 3 times. If you find that you're extremely tight in this area, you might want to alternate this exercise with the ball-work.
Я специалист по работе с телом, специализируюсь на постуральных и ортопедических проблемах, и я часто работаю с поясничными мышцами. Существует определённая связь между поясничными мышцами и сколиозом.
Хронически напряженные поясничные мышцы разрушают в хлам нижний отдел спины. Когда верхние волокна поясничной мышцы напряжены, это ставит позвоночник в положение гиполордоза (уменьшение естественного изгиба спины). Когда нижние волокна поясничной мышцы напряжены, это ставит позвоночник в положение гиперлордоза (увеличение естественного изгиба спины). Часто при сколиозе одна часть более напряжена, чем другая, или одна сторона напряжена вверху, а вторая - внизу. Это будет приводить к крутящему эффекту поясничного отдела позвоночника и таза.
Существует способ дотянуться до поясничных мышц самостоятельно, но будьте осторожны. Если что-то не так с брюшной полостью, типа кишечных проблем, это будет противопоказанием. Нужно взять надувной мячик чуть больше чем теннисный, положить его на пол и лечь на него лицом вниз так, чтобы мяч был с одной стороны и внизу живота. Расслабьтесь на нём своим весом пока не почувствуете место напряжения или ощущение жара и напряжения. Вы должны продолжать опускать свой вес по мере расслабления поясничной мышцы. Затем нужно передвинуть мячик немного в сторону и вниз. Каждый раз, когда почувствуете напряжение или жар, позвольте телу медленно опуститься на мячик по мере отпускания напряжения. Проделать для обеих сторон.
Мячик должен быть около 10 см. в диаметре. Если у вас хрупкое сложение, можно взять мячик поменьше, если крупное - то мячик покрупнее. Но до настоящего момента для большинства моих клиентов прекрасно работал 10-сантиметровый.
Другой хороший способ расслабить поясничную мышцу - сделать это непрямым способом. Мышцы работают в парах. Чтобы сустав двигался, она мышцы должна сокращаться, а другая - расслабляться. Если вы сократите мышцы, противоположные поясничным, это заставит поясничные мышцы расслабиться до какой-то степени (снова - если вы чувствуете, что с вашим телом что-то не так, пожалуйста, прекратите практику). Нужно лечть на спину с согнутыми коленями. Подтяните одно колено к груди и обхватите его руками. Теперь старайтесь вернуть ногу в исходное положение, в то же время притягиваю её в груди. Вы сокращаете задние мышцы бедра (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris, http://www.anatomix.ru/anat/anat211.htm), которые являются главными его разгибателями. Задержите напряжение примерно на 10 секунд, а затем перемените стороны. Повторите по 3 раза для каждой стороны. Если вы обнаружите, что у вас очень стльное напряжение в этом районе, можно чережлвать это упражнение с работой с мячом.
http://www.todayschiropractic.com/issues/archives/jul_aug_02/psoas.html
Release Procedures
The next step is to release this contracture, which is accomplished in the following manner: Determine the midway point between the umbilicus and the ASIS. Then, place two fingers (index and middle finger together at this point of reference) there, and you are now going to apply pressure, which will be either clockwise or counterclockwise, depending on the side of involvement.
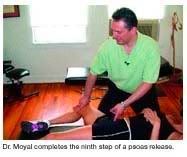
If you find a left-sided contracture, you would stand on the supine patient’s left side, and place the two fingers of your right hand on that reference point. Then, have the patient bend their knee. With your left hand on their knee, you are going to ask them to take a deep breath in (you also want to mention that this will probably not feel too good, but that the results will be astonishing and well worth the temporary discomfort).
As the patient takes in the deep breath and releases it slowly, you are going to do two things simultaneously. Your left hand is going to diagonally abduct and push down their leg, using the knee as a leverage point. While using the two fingers of your right hand, you are going to push into the reference point from anterior to posterior (into the psoas) while rotating your fingers clockwise. You will be using the left hand to push their knee down to create a stretching and elongation of the psoas muscle, releasing the involved contracture.
Although there is some discomfort involved, after you finish the next procedure, have the patient walk around the room. You will typically hear from the patient how much better it already feels and that much of the pressure is gone from their hip, low back, mid and upper back, neck and shoulders!
The next step is to release the third and fourth lumbar in lateral flexion and rotation minimally (there may also be some flexion and extension fixation involvement) because of their part in the involvement of the affected psoas muscle.
The last step is to release the superior tibia/fibula joint on the same side as the involved psoas, because of the torque and pressure exerted by the tensor fascia lata, which disappears upon releasing that joint. This is accomplished by placing the top part of your proximal thumb under the patient’s knee (lateral side) fibula on the involved psoas side. Then you flex their knee into your thumb while, with your other hand on their ankle, applying a posterior force against your right thumb. This causes a counter-pressure and that joint to release, further releasing the tensed TFL. Now, have the patient walk around and notice the changes.
This appears very simplistic, yet chiropractors rarely ever bother to check the psoas. As a result, the patient is left with a recurring chronic problem, which mimics the appearance of a scoliosis upon physical and X-ray examinations.
As you begin to release the psoas muscle in your patients, you will personally see some amazing results, as well as the disappearance of many so-called scoliotic lumbar curvatures. It is part of the success formula. Check the psoas on everyone until you get a feel for the history and pattern of appearance of contracture, and then watch the results unfold.
Процедура освобождения
Найдите середину между пупком и передним верхним краем подвздошной кости. Затем положите два пальца (указательный и средний в указанную точку) - теперь вы готовы прикладывать усилие, которое может быть направлено по часовой стрелке либо против часовой стрелки, в зависимости от стороны работы.
Если вы найдёте контрактуру с левой стороны, вы должны встать с левой стороны лежащего на спине пациента и положить два пальца своей правой руки на указанную точку. Затем пациент должен согнуть колено. Положите свою левую руку ему на колено и попросите его сделать глубокий вдох.
Пациент глубоко вдыхает и медленно выдыхает, а вы в это время должны сделать две вещи одновременно. Ваша левая рука по диагонали отводит и направляет вниз его ногу, используя колено как точку опоры рычага. Двумя пальцами правой руки надавите на указанную точку спереди назад, вращая пальцы по часовой стрелке. Левой рукой нужно отводить колено вниз, растягивая и удлинняя поясничную мышцу.
Выполнение этой манипуляции сопровождается дискомфортом, и после её окончания надо попросить пациента пройтись по комнате. Обычно вы сразу услышите насколько легче он себя уже чувствует и как сильно уменьгилось напряжение в тазу, нижнем, среднем и верхнем отделах спины, плечах и шее.
Следующий шаг - освободить третий и четвертый поясничные позвонки боковым сгибанием и вращением, т.к. они могут быть сдвинуты поясничной мышцей.
Последний шаг - освободить коленный сустав на воздействованной стороне, из-за вращающего момента и давления, которое даёт Напрягатель широкой фасции бедра, musculus tensor fasciae latae (http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24852.html), и которое исчезает после освобождения этого сустава. Это делают, размещая верхнюю часть большого пальца под колено пациента (боковую часть) fibula на той стороне, над которой работаете. Затем вы сгибаете его колено, зажимая большой палец, с другой рукой на его лодыжке, прикладывая направленную кзади силу. Это даёт противополодно направленное давление, и сустав освобожлается, освобождая также Напрягатель широкой фасции бедра. Теперь скажите пациенту пройтись и обратить внимание на изменения.
Это кажется очень простым, но хиропракторы редко даже беспокоятся о том, чтобы проверить поясничную мышцу. В результате пациент остаётся с хроническими возвращающимися болями, а позвоночник на рентгене выглядит сколиотичным.
По мере того, как вы начнете практиковать освобождение поясничной мышцы у своиз пациентов, вы увидите потрясающие результаты, а также исчезновние многих так называемых сколиотичных поясничных искривлений. Проверяйте поясничную мышцу у всех пока не убедитесь, что она не участвует в создании контрактуры.
http://thewinger.com/words/category/psoas/
What is the best treatment for a psoas problem?
The muscle is not outwardly palpable such as the hamstring or biceps muscle. You really need to dig deep to get to the psoas. Stretching helps but rarely eliminates the problem. I have found Active Release Technique to be the most successful treatment in the case of Psoas dysfunction. ART allows you to fully stretch the muscle while breaking down scar tissue and adhesions that develop from repetitive use.
IMPORTANT TIPS
Situps- Make sure to isolate your abs. Many times you recruit the hip flexor or psoas and it takes away from the Abs. This improper situp can cause injury to the psoas. How do I do that?
Place both feet on a wall and do a crunch. Feel the difference.
Ещё упражнения - просмотрены мной менее внимательно, оставляю ссылки до кучи:
http://www.easyvigour.net.nz/fitness/h_PsoasStretch.htm
http://www.somatics.com/psoas.htm
http://www.laybak.com/about.htm - хорошая картинка люмбо-сакрального региона.
http://www.exrx.net/WeightExercises/GluteusMaximus/LVLyingHipExtension.html - упражнения на расслабление пояснично-подвздошной мышцы
http://www.emedicine.com/sports/TOPIC52.HTM
Acute injury and overuse injury are the 2 main causes of iliopsoas tendinitis. The acute injury typically involves an eccentric contraction of the iliopsoas muscle, but also may be due to direct trauma. Overuse injury may occur in activities involving repeated hip flexion or external rotation of the thigh. Activities that may predispose to iliopsoas tendinitis include dancing, ballet, resistance training, rowing, running (particularly uphill), track and field, soccer, and gymnastics.
During the adolescent growth spurt, the hip flexors tend to become relatively inflexible. This inflexibility can lead to problems in younger athletes because stress placed on the iliopsoas musculotendinous unit increases and general biomechanics are altered. Tightness of the iliopsoas, tensor fascia lata, or rectus femoris can lead to inhibition of the gluteus maximus, allowing for an anterior pelvic tilt. This in turn leads to adverse affects on the kinetic chain. Excessive anterior tilt can lead to increased lumbar lordosis with resultant stress on the lower lumbar discs, facet joints, and sacroiliac joints and may result in increased knee flexion at heel strike and during midstance phases of the gait cycle. The subsequent increase in eccentric load across the knee extensor mechanism may result in patellar tendon injuries. With increased knee flexion, compressive forces at the patellofemoral contact surface increase and may predispose to patellofemoral problems.
Перевод francuz_bel, коррекция моя.
Острая травма и травма переиспользования являются двумя основными причинами тендинита (Тенденит (tendinitis) - воспаление сухожилия). Острая травма обычно является следствием необычного сокращения подвздошно-поясничной мышцы, но также может случиться по причине прямой травмы. Травма переиспользования может случиться в результате действий, включающих в себя повторяющиеся сгибания бёдер или разворот бёдер наружу. Действия, располашающие к тендиниту: танцы, балет, тренировки сопротивлению, гребля, бег (особенно в гору), лёгкая атлетика, футбол и гимнастика.
Во время подросткового скачка роста сгибатели бедра имеют тенденцию к потере гибкости. Эта потеря гибкости может привести к проблемам у молодых атлетов, т.к. нагрузка оказываемая на подвздошно-поясничную мускулатуру, возрастает и общая биомеханика меняется. Напряжение пояснично-подвздошной мышцы, напрягателя широкой фасции бедра, или прямой мышцы бедра может привести к угнетению ягодичной мышцы, приводя к наклону таза вперёд. Это, в свою очередь, приводит к неблагоприятным эффектам кинетической цепочки. Чрезмерный наклон вперёд может приводить к усиленному поясничному лордозу с проистекающим давлением на нижние поясничные диски, суставы и крестцово-подвздошные суставы и может приводить к увеличению сгибания коленей в момент удара пятки о землю и в средгий момент цикла шага. Последующее усиление необычной нагрузки на коленный разгибательный механизм может привести к повреждениям надколенного сухожилия. С усилением сгибания колена компрессионные силы в месте соединения прямой мышцы бедра с надколенным сухожилием возрастают, что предрасполагает проблемам в этом месте.
Всё это входит в прямое притиворечие с информацией отсюда http://zakazdiplom.ru/show_work.php?work=12033 или http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/28307.html
Этот метод лечения способствует уменьшению наклона поясничного отдела позвоночника на стороне тренировки пояснично-подвздошной мышцы.
http://blog.360.yahoo.com/blog-yQEIEIs8er7tz9YyK.Ak2NxAs1XJ
In the 1950’s Lawrence Jones, D.O. discovered by accident that when he placed the body into a comfortable position pain and dysfunction would heal quickly. He initially called this approach to pain “spontaneous release by positioning.” This work is now known generically as Positional Release or as the "fold and hold" technique." In most cases the position created is the original position of injury or an abnormal bony relationship. NRT is a variation of positional release that has been developed for use by Massage professionals.
http://www.naturalreflexes.com/pages/Psoas.html
http://www.squidoo.com/psoas
Understanding and Releasing the Psoas Muscle
Понятие и освобождение поясничной мышцы
What keeps the psoas in contraction?
The psoas will stay contracted because of postural habits and trauma. The way we stand, walk and sit can distort the it. If we walk or stand with our chin in an overly forward position the muscle will tighten. Ida Rolf wrote, "a deteriorated psoas" chronically flexes the body at the level of the groin, so that it prevents truly erect posture.?7 Sitting through much of the day the psoas shortens to keep us bio mechanically balanced in our chairs. Over time we develop a "normal" way of holding the psoas that is dysfunctional.
Unresolved trauma can keep the psoas short and reactive. After a traumatic occurrence animals will release their protective responses by shaking. Humans often bypass this release response and hold the trauma in their bodies.8 Until the psoas is released the muscle may stay contracted and fearful and go into further shortening and spasm very easily.
Что держит поясничную мышцу сокращенной?
Поясничная мышца остается сокращенной (стянутой) в результате пагубного воздействия неправильной осанки или травмы. То, как мы стоим, идет или сидим могут ухудшать состояние поясничной мышцы. Если мы ходим или стоим с чрезмерно выпяченным вперед подбородком, то мышца будет сокращаться. Ида Рольф написала “истощенная поясничная мышца” хронически изгибает тело на уровне паховой области так, что это препятствует по-настоящему полному выпрямлению осанки. Долгое сидение на протяжении дня сокращает поясничную мышцу чтобы поддерживать нас в биомеханическом балансе на наших стульях. Через какое-то время мы создаем “нормальный”, “обычный” стереотип держания мышцы, который не является правильным.
Непролеченная до конца травма может держать мышцу сокращенной. Животные после травматического эпизода снимают результаты действия защитного инстинкта встряхиванием. Люди часто обходят эти инстинкты и держат последствия травмы в своем теле. Пока поясничная мышца не расслаблена, она может оставаться сокращенной и напряженной, и дальше легко спазмироваться и укорачиваться.
Releasing the Psoas Muscle with Natural Reflex Therapy
How does Natural Reflex Therapy release the psoas?
NRT creates a comfortable position for the psoas that typically shortens the muscle. Through fine tuning and client feedback the best position is discovered. Within seconds the body may begin to release spasm, restore normal muscle tone, increase circulation, remove pressure on nerves, and allow bones and joints to move freely. Often, by recreating the original strain the muscle is restored to a normal range of contraction and relaxation.9 To keep the psoas in its normal range, we must also place the pelvis and spine into positions that restore optimum biomechanical function. All the energy and attention that was used to deal with pain is now available to the body's healing process.
These positions stimulate specific reflexes in the body that help to restore a better balance to the psoas, pelvis and lumbar vertebrae. The reflexes that we stimulate are found within the proprioceptive nervous system, which monitors and helps coordinate all muscular movements. These reflexes give us our sense of our shape, density, quality and speed of movement, and effort. .
Because this method is indirect there is less chance of re-traumatizing the muscle or stimulating new spasm. Rather than trying to force the muscle to change, the reflexes that hold the psoas in contraction are allowed to reset a new state of structure and function. When the reflexes learn/remember how to restore balance there is a greater chance of long lasting or permanent changes. When the psoas has freedom of movement and function, the client is encouraged to use movements and exercises that will prevent future occurrences.
Over time the client can learn to maintain and control the psoas, that hidden prankster, and its role in the essential balance of our core structures. Referred pain patterns are discontinued when the seat of the disturbance is relieved. The client can begin to remember the sense or feeling of a dynamically neutral orientation as comfort. With specific exercise and better posture they can keep the psoas from shortening. Conditions recover and the possibility of elegance is made more possible. Our capacity to protect ourselves, without holding trauma, improves, particularly when other forms of therapy are added to the process. With renewed structural integrity, enhanced circulation, unimpinged nerve function, and flowing chi we are sustained at a higher level of health.
Лечение пояснично-подвздошной мышцы методом натуральной рефлексотерапии (НРТ)
Как это возможно?
НРТ создает комфортные условия для мышцы, которая обычно сокращена. С помощью качественной настройки и обратной связи с клиентом находится наилучшая позиция. В течении нескольких секунд тело может начать справляться со спазмом, восстанавливать нормальный мышечный тонус, усиливать циркуляцию крови, избавляться от нервного напряжения, и позволять костям и суставам двигаться свободнее. Часто мышца возвращется в нормальный режим сокращения и напряжения путём воспроизводства первоначального напряжения. Чтобы поддерживаться мышцу в нормальном тонусе мы должны также распологать таз и спину в положения, которые обеспечивают оптимальное выполнение биомеханических функций. Вся энергия и внимание, которые были использованы в борьбе с болью сейчас имеются в наличии для того чтобы запустить излечивающие силы организма.
Такие положения стимулируют специфические рефлексы в организме которые помогают восстановить лучший баланс мышцы, таза и поясничных позвонков. Рефлексы, которые мы стимулируем, основаны на проприоцептивной нервной системе, которая наблюдает и помогает координировать все движения мышц. Эти рефлексы дают нам чувство нашего тела, плотности, качества и скорости движения и усилий.
Проприоцептор - рецепторы, которые находятся в основном в мышцах, связках, суставах, и во внутреннем ухе, определяют движение или положение тела или конечности, отвечая на стимулы, происходящие внетри организма.
Т.к. этот метод непрямой, то получается меньше шансов еще раз травмировать мышцы или стимулировать новый спазм. Лучше чем пытаться форсировать изменение мышц, ма позволяем рефлексам, которые удерживают поясничную мышцу в напряжении, установить новое положение скелета и функций. Когда мы изучаем или вспоминаем как восстановить баланс на уровле рефлексов, появляется наилучший шанс длительных или постоянных изменений. Когда поясница свободна в движениях и функционирует нормально, клиент поддерживает движения и упражнения, которые предупреждают будущие происшествия.
Через какое-то время клиент может научиться поддерживать и контролировать поясничную мышцу, этого скрытого шутника, и ее роль в балансе нашей ключевой структуры. Вышеупомянутые болевые паттерны прекращаются когда место возбуждения расслабляется. Клиент может начать вспомнать чувство или ощущение динамически нейтрального положения как комфорт. С помощью специальных упражнений и хорошей осанки они могут уберечь поясничную мышцу от спазмирования. Эти условия возвращают и возможность грации в движениях. Наша способность защищать себя, отпуская травму, улучается особенно тогда когда другие формы терапии добавлены к процессу. С обновленной целостностью структуры, улучшенной циркуляцией, освобождённой от ущемлений нервной функцией и большим количеством энергии мы поддерживаемся на высочайшем уровне здоровья.
http://www.menshealth.com/cda/article.do?site=MensHealth&channel=fitness&category=sports.injuries&conitem=294144debb8a3010VgnVCM100000cfe793cd____
What is the cause of Lordosis?
Some muscles around the hip and spine become tight and some become weak and stretched, causing an imbalance. The muscles that are often tight are:
Trunk extensors (erector spinae and quadratus lumborum).
Hip flexors (in particular the iliopsoas muscle).
These muscles require stretching.
The muscles that are often weak and stretched are:
Abdominal muscles (rectus abdominus, internal oblique and external oblique)
Hip extensors (hamstrings and gluteus maximus).
These muscles require strengthening.
Что является причиной лордоза
Некоторые мышцы бедра и спины сжимаются, а некоторые становятся слабыми и растянутыми, что ведёт к дисбалансу.
Мышцы, которые часто сжимаются: разгибатели корпуса (erector spinae и quadratus lumborum, http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24805.html) и сгибатели бедра, в частности, подвздошно-поясничная мышца, http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24852.html. Этим мышцам часто требуется растяжка.
Мышцы, которые часто слабы и растянуты: мышцы живота (rectus abdominus, internal oblique и external oblique, http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/26243.html) и разгибатели бедра (hamstrings (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris, http://www.anatomix.ru/anat/anat211.htm и gluteus maximus http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24852.html). Эти мышцы нуждаются в укреплении.
http://www.scoliosis.org/forum/archive/index.php/t-179.html
I'm a bodyworker specializing in postural and orthopedic concerns, and I frequently work with the psoas muscle. There is a definite correlation between the psoas and scoliosis.
A chronically tight psoas will wreak havoc with the lower spine. When the upper fibers of the psoas are tight, it tends to put the spine into hypo-lordosis (decreases the natural curve of the lower spine.) When the lower fibers of the psoas are tight, it tends to place the lumbar spine into hyperlordosis (an increase of that curve.) Frequently, in scoliosis, one side is tighter than the other, or one side is tight on top and the other side tight on the bottom. This will lead to a torquing effect of the lumbar spine and pelvic girdle.
There is a way to access the psoas yourself, but please be careful. I've never met you, and I'm not sure if there would be any contraindications in your case. Anything wrong in the abdomen, like intensinal problems would be a contraindiacation. Basically, you take an inflatable ball just a little larger than a tennis ball, place it on the floor, and lay on it. You'll be face-down, and the ball will be just to the side of your belly button. Ease your weight down on it until you feel an area of tension or a hot, crampy sensation. You would continue to ease your weight down on it as the psoas loosens up. Then you would move the ball out and down a bit. Any time you find tension or the hot-crampy sensation, allow your body weight to gently ease down onto the ball as the tension releases. Do both sides.
I've seen balls the proper size at Walmart in their huge bins and also at pet stores as dog toys. Some school supply places carry them. You're looking for something with about a 4" diameter. If you're very small framed, you might go a little smaller, or if you're very large, then maybe something slightly larger. But so far, with most of my clients, the 4" ball seems to work very well.
Another good way to get the psoas to release some tension is to trigger it to do so indirectly. Muscles work in pairs. To move any joint, one muscle has to contract while another relaxes. If you contract the muscles opposite the psoas, it will trigger the psoas to relax some. (As you follow these directions, if anything feels wrong to your body, please discontinue. As I've said, I've never met you, and I don't know what particular contraindications might apply in your case.) You'd lie on your back with knees bent. Bring one knee toward your chest and clasp your hands behind your knee. Try to push your foot back toward the floor while your arms are trying to pull that leg closer to your chest. You're contracting your hamstrings, which are the main hip extensors. Hold the tension for about 10 seconds and then switch sides. Repeat so that you've done each side about 3 times. If you find that you're extremely tight in this area, you might want to alternate this exercise with the ball-work.
Я специалист по работе с телом, специализируюсь на постуральных и ортопедических проблемах, и я часто работаю с поясничными мышцами. Существует определённая связь между поясничными мышцами и сколиозом.
Хронически напряженные поясничные мышцы разрушают в хлам нижний отдел спины. Когда верхние волокна поясничной мышцы напряжены, это ставит позвоночник в положение гиполордоза (уменьшение естественного изгиба спины). Когда нижние волокна поясничной мышцы напряжены, это ставит позвоночник в положение гиперлордоза (увеличение естественного изгиба спины). Часто при сколиозе одна часть более напряжена, чем другая, или одна сторона напряжена вверху, а вторая - внизу. Это будет приводить к крутящему эффекту поясничного отдела позвоночника и таза.
Существует способ дотянуться до поясничных мышц самостоятельно, но будьте осторожны. Если что-то не так с брюшной полостью, типа кишечных проблем, это будет противопоказанием. Нужно взять надувной мячик чуть больше чем теннисный, положить его на пол и лечь на него лицом вниз так, чтобы мяч был с одной стороны и внизу живота. Расслабьтесь на нём своим весом пока не почувствуете место напряжения или ощущение жара и напряжения. Вы должны продолжать опускать свой вес по мере расслабления поясничной мышцы. Затем нужно передвинуть мячик немного в сторону и вниз. Каждый раз, когда почувствуете напряжение или жар, позвольте телу медленно опуститься на мячик по мере отпускания напряжения. Проделать для обеих сторон.
Мячик должен быть около 10 см. в диаметре. Если у вас хрупкое сложение, можно взять мячик поменьше, если крупное - то мячик покрупнее. Но до настоящего момента для большинства моих клиентов прекрасно работал 10-сантиметровый.
Другой хороший способ расслабить поясничную мышцу - сделать это непрямым способом. Мышцы работают в парах. Чтобы сустав двигался, она мышцы должна сокращаться, а другая - расслабляться. Если вы сократите мышцы, противоположные поясничным, это заставит поясничные мышцы расслабиться до какой-то степени (снова - если вы чувствуете, что с вашим телом что-то не так, пожалуйста, прекратите практику). Нужно лечть на спину с согнутыми коленями. Подтяните одно колено к груди и обхватите его руками. Теперь старайтесь вернуть ногу в исходное положение, в то же время притягиваю её в груди. Вы сокращаете задние мышцы бедра (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris, http://www.anatomix.ru/anat/anat211.htm), которые являются главными его разгибателями. Задержите напряжение примерно на 10 секунд, а затем перемените стороны. Повторите по 3 раза для каждой стороны. Если вы обнаружите, что у вас очень стльное напряжение в этом районе, можно чережлвать это упражнение с работой с мячом.
http://www.todayschiropractic.com/issues/archives/jul_aug_02/psoas.html
Release Procedures
The next step is to release this contracture, which is accomplished in the following manner: Determine the midway point between the umbilicus and the ASIS. Then, place two fingers (index and middle finger together at this point of reference) there, and you are now going to apply pressure, which will be either clockwise or counterclockwise, depending on the side of involvement.

If you find a left-sided contracture, you would stand on the supine patient’s left side, and place the two fingers of your right hand on that reference point. Then, have the patient bend their knee. With your left hand on their knee, you are going to ask them to take a deep breath in (you also want to mention that this will probably not feel too good, but that the results will be astonishing and well worth the temporary discomfort).
As the patient takes in the deep breath and releases it slowly, you are going to do two things simultaneously. Your left hand is going to diagonally abduct and push down their leg, using the knee as a leverage point. While using the two fingers of your right hand, you are going to push into the reference point from anterior to posterior (into the psoas) while rotating your fingers clockwise. You will be using the left hand to push their knee down to create a stretching and elongation of the psoas muscle, releasing the involved contracture.
Although there is some discomfort involved, after you finish the next procedure, have the patient walk around the room. You will typically hear from the patient how much better it already feels and that much of the pressure is gone from their hip, low back, mid and upper back, neck and shoulders!
The next step is to release the third and fourth lumbar in lateral flexion and rotation minimally (there may also be some flexion and extension fixation involvement) because of their part in the involvement of the affected psoas muscle.
The last step is to release the superior tibia/fibula joint on the same side as the involved psoas, because of the torque and pressure exerted by the tensor fascia lata, which disappears upon releasing that joint. This is accomplished by placing the top part of your proximal thumb under the patient’s knee (lateral side) fibula on the involved psoas side. Then you flex their knee into your thumb while, with your other hand on their ankle, applying a posterior force against your right thumb. This causes a counter-pressure and that joint to release, further releasing the tensed TFL. Now, have the patient walk around and notice the changes.
This appears very simplistic, yet chiropractors rarely ever bother to check the psoas. As a result, the patient is left with a recurring chronic problem, which mimics the appearance of a scoliosis upon physical and X-ray examinations.
As you begin to release the psoas muscle in your patients, you will personally see some amazing results, as well as the disappearance of many so-called scoliotic lumbar curvatures. It is part of the success formula. Check the psoas on everyone until you get a feel for the history and pattern of appearance of contracture, and then watch the results unfold.
Процедура освобождения
Найдите середину между пупком и передним верхним краем подвздошной кости. Затем положите два пальца (указательный и средний в указанную точку) - теперь вы готовы прикладывать усилие, которое может быть направлено по часовой стрелке либо против часовой стрелки, в зависимости от стороны работы.
Если вы найдёте контрактуру с левой стороны, вы должны встать с левой стороны лежащего на спине пациента и положить два пальца своей правой руки на указанную точку. Затем пациент должен согнуть колено. Положите свою левую руку ему на колено и попросите его сделать глубокий вдох.
Пациент глубоко вдыхает и медленно выдыхает, а вы в это время должны сделать две вещи одновременно. Ваша левая рука по диагонали отводит и направляет вниз его ногу, используя колено как точку опоры рычага. Двумя пальцами правой руки надавите на указанную точку спереди назад, вращая пальцы по часовой стрелке. Левой рукой нужно отводить колено вниз, растягивая и удлинняя поясничную мышцу.
Выполнение этой манипуляции сопровождается дискомфортом, и после её окончания надо попросить пациента пройтись по комнате. Обычно вы сразу услышите насколько легче он себя уже чувствует и как сильно уменьгилось напряжение в тазу, нижнем, среднем и верхнем отделах спины, плечах и шее.
Следующий шаг - освободить третий и четвертый поясничные позвонки боковым сгибанием и вращением, т.к. они могут быть сдвинуты поясничной мышцей.
Последний шаг - освободить коленный сустав на воздействованной стороне, из-за вращающего момента и давления, которое даёт Напрягатель широкой фасции бедра, musculus tensor fasciae latae (http://healthy-back.livejournal.com/24852.html), и которое исчезает после освобождения этого сустава. Это делают, размещая верхнюю часть большого пальца под колено пациента (боковую часть) fibula на той стороне, над которой работаете. Затем вы сгибаете его колено, зажимая большой палец, с другой рукой на его лодыжке, прикладывая направленную кзади силу. Это даёт противополодно направленное давление, и сустав освобожлается, освобождая также Напрягатель широкой фасции бедра. Теперь скажите пациенту пройтись и обратить внимание на изменения.
Это кажется очень простым, но хиропракторы редко даже беспокоятся о том, чтобы проверить поясничную мышцу. В результате пациент остаётся с хроническими возвращающимися болями, а позвоночник на рентгене выглядит сколиотичным.
По мере того, как вы начнете практиковать освобождение поясничной мышцы у своиз пациентов, вы увидите потрясающие результаты, а также исчезновние многих так называемых сколиотичных поясничных искривлений. Проверяйте поясничную мышцу у всех пока не убедитесь, что она не участвует в создании контрактуры.
http://thewinger.com/words/category/psoas/
What is the best treatment for a psoas problem?
The muscle is not outwardly palpable such as the hamstring or biceps muscle. You really need to dig deep to get to the psoas. Stretching helps but rarely eliminates the problem. I have found Active Release Technique to be the most successful treatment in the case of Psoas dysfunction. ART allows you to fully stretch the muscle while breaking down scar tissue and adhesions that develop from repetitive use.
IMPORTANT TIPS
Situps- Make sure to isolate your abs. Many times you recruit the hip flexor or psoas and it takes away from the Abs. This improper situp can cause injury to the psoas. How do I do that?
Place both feet on a wall and do a crunch. Feel the difference.
Ещё упражнения - просмотрены мной менее внимательно, оставляю ссылки до кучи:
http://www.easyvigour.net.nz/fitness/h_PsoasStretch.htm
http://www.somatics.com/psoas.htm
http://www.laybak.com/about.htm - хорошая картинка люмбо-сакрального региона.
http://www.exrx.net/WeightExercises/GluteusMaximus/LVLyingHipExtension.html - упражнения на расслабление пояснично-подвздошной мышцы