DHEA

For Women:

Used by body builders, makes sense because it feeds into testosterone pathway and T is good for building muscle:

Homosexuals have less:

WOW THIS IS INTERESTING: from www.anthropogeny.com/AIDS%20and%20DHEA.htm
My explanation of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is derived directly from my foundation hypothesis that DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone) is necessary for duplication and transcription of DNA . Since all tissues depend on DNA, I suggest all tissues depend on DHEA. Therefore, it follows that all tissues compete for a limited supply of DHEA. In 1985, I copyrighted the idea that low DHEA increases vulnerability to infection by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and AIDS. In 1989, it was reported that DHEA is low in men infected with the HIV and lower in those with AIDS compared to healthy seronegative (virus free) controls (Journal of the American Medical Association 1989; 261: 1149). The key to understanding HIV infection and AIDS is that the immune system cannot capture enough DHEA to mount a satisfactory response to the HIV. I am convinced that treatment with DHEA may be the cure. I suggest the symptoms of AIDS are actually symptoms of severe loss of DHEA.
Another non-AIDS study reported that CD4+ lymphocytes declined and a form of CD8+ lymphocytes increased upon use of micronized DHEA (Am. J. Ob Gyn. 1993; 169: 1536). That is, large increases in DHEA in the blood reduce the total number of CD4+ lymphocytes and increase the total number of CD8+s. This pattern of changes in lymphocytes is considered typical of HIV infection. For example, one study found this pattern in HIV infection and also in "infectious mononucleosis but not in HIV non-converters or HIV-seronegative patients" (AIDS 1995; 9: 561). (Remember that DHEA was not low in seronegative (non-infected, healthy) individuals in the JAMA study above.) Another study found differences in a different subset of CD8+ lymphocytes as well as reductions in CD4+ (AIDS 1995; 9: 421). In fact, the clinical features of infections by Epstein-Barr virus or cytomegalovirus resemble HIV infection, and specific antibody tests and history (clinical suspicion) are often necessary to distinguish these viral infections from each other (AIDS 1995; 9: 562). Also in the same journal: "The significance of the cytotoxic [subset of CD8+s] T-cell response in primary HIV infection is not known. However, increased CD8+CD38+ cells are associated with more rapid HIV disease progression and increased CD8+CD38- cells with stable CD4+ lymphocyte counts over time" (AIDS 1995; 9: 562). The important characteristic is that total CD4+s decline and total CD8+s increase in response to viral infections and increases in DHEA. I suggest the common link in total lymphocyte response and clinical symptoms is DHEA response. I suggest the differences in lymphocyte responses rest on the kind of virus and the individual's ability to respond with DHEA. Since the HIV kills CD4+ lymphocytes and increased DHEA also reduces CD4+s, the CD4+ decline is exaggerated during HIV disease and AIDS. This excessive reduction in CD4+s, above the expected CD4+ kill rate caused by the HIV, was noticed in 1988, but was not explained. The combination of HIV and DHEA on CD4+s is the reason. ("Micronized" DHEA is no longer considered to be a necessary form of DHEA for use.)
"Thus, it has been hypothesized that in addition to a direct HIV-induced cytopathic effect on a given T4 [CD4] cell, other potential mechanisms of T4 depletion may be operable." (Science 1988; 239: 619)
I suggest DHEA naturally increases in response to viral and bacterial infections in order to increase availability of DHEA for the immune system. The initial increase is probably derived from DHEA sulfate (DHEAS) in the blood: "DHA [DHEA] never reached zero concentration in plasma, whereas cortisol did. This is explained by the contribution to DHA by hydrolysis of the relatively abundant circulating DHA sulfate [DHEAS]. Because of the low plasma concentration a high degree of biological activity can be implied for DHA, the function of which is at present unknown" (J. Clinical Endocrinology 1971; 33: 87). Those who progress to AIDS, however, cannot maintain the DHEA response. In one study of AIDS, DHEA increased early during HIV disease, but all participants who progressed to full-blown AIDS had low levels of DHEAS (J. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 1992; 5: 841). They could not maintain their DHEA response to HIV, because they did not have enough DHEAS. (JAIDS is now called the Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes and Human Retrovirology. Do not confuse this journal with the one called AIDS.)
... more from same site:
Men produce much more testosterone than women. Black women produce more testosterone than white women (unpublished results from the University of Tennessee, Medical School). Hence, men are more easily infected than women, and black women are more easily infected than white women. Testosterone is significantly higher in healthy black males compared to healthy white males (J. National Cancer Institute 1986; 76: 45). Black males produce more testosterone than any other group. Therefore, higher levels of testosterone increase susceptibility to HIV infection and worsen the symptoms of AIDS. It is known that "AIDS patients are disproportionately black (26%) and Hispanic (13%), compared with the proportions of blacks (12%) and Hispanics (6%) in the U.S. population." (JAMA 1989; 261: 201) and "The prevalence [of HIV] among black teenaged applicants (1.06 per 1000) was greater than among white (0.18 per 1000) or Hispanic (0.31 per 1000) teenaged applicants [to the military]" (JAMA 1990; 263: 2074). This also explains the "...unexpected finding that under the same social conditions, blacks are apparently infected more readily by Mycobacterium tuberculosis than whites" (The New Eng. J. Med. 1990; 322: 422). Increased HIV seropositivity in blacks and Hispanic intravenous drug abusers (IVDAs) is not due to more needle sharing; white IVDAs share needles more frequently than these minorities (JAMA 1987; 258: 1475).
Women are known to have a more aggressive immune system. I suggest this is due to lower testosterone and higher DHEA in women. Women are known to have less DHEAS than men. This may be due to the "X-linked steroid sulfatase" found on the X chromosome. (A steroid sulfatase removes the sulfate group from a steroid sulfate; this makes DHEA out of the steroid sulfate, DHEAS.) The unusual aspect of this steroid sulfatase is that it is active on both X chromosomes (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 1987; 84: 4519). Women have two X chromosomes, men one. Since DHEAS may be the only steroid hormone produced as a sulfate, women would produce more DHEA than men. Therefore, females should react with a greater DHEA response upon HIV infection. Women are able to produce more DHEA from DHEAS, and white women produce the least testosterone of all of these groups. This explains why "Prevalence [of HIV infection] was lowest in white women" (Science 1995; 270: 1374). The ratio of DHEA to testosterone affects infection rates dramatically. ("Dehydroepiandrosterone ...is uniquely sulfated (DHEAS) prior to export into the plasma..." (European J. Immunology 1990; 20: 793; also see Review of Medical Physiology, 16th. ed., Lange Medical Publications, 1993, page 329.)
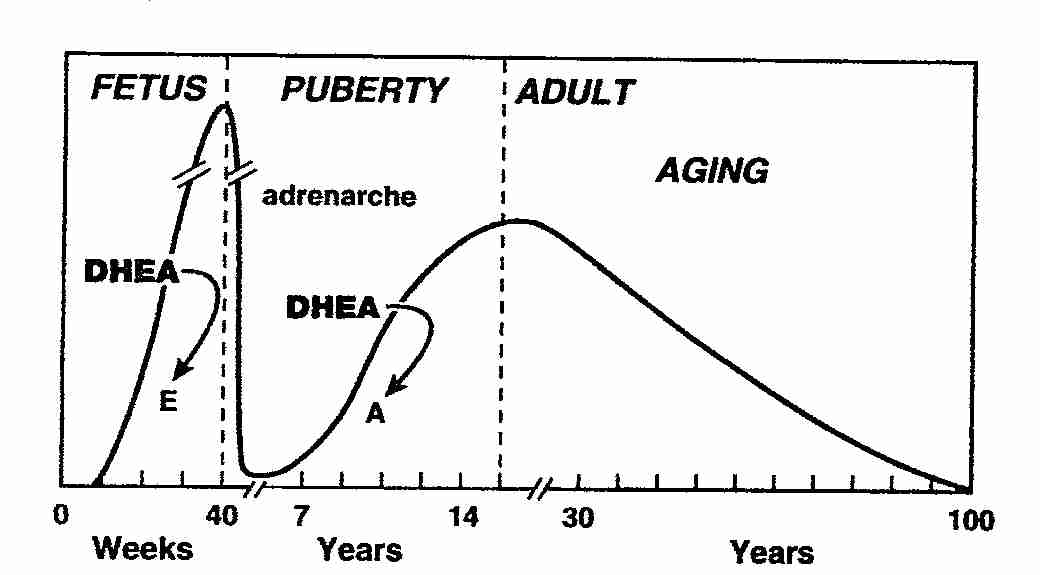
Men are more readily infected by the HIV than women. Since DHEA naturally begins to decline around age 25 (Period E), mortality from AIDS should concentrate in men over 25. The so-called "incubation period" of AIDS results from early infection, followed by sickness and death, which begins to occur when DHEA begins to decline. Consider the chart of DHEA during the human life-span, above, and the following quotations.
"More than 90% of the AIDS-related mortality occurs in men, with nearly 75% in those 25 to 44 years old." (Science 1988; 239: 611)
"Once AIDS has developed, age continues to be a factor for the worsening of the disease. Large studies in New York and San Francisco have shown decreased survival times for persons with AIDS over 40 years of age." (J. Gerontology 1990; 45: M77)
In 1985, I hypothesized that reduced DHEA causes vulnerability to AIDS and that homosexual males produce low DHEA, because of conversion of part of their DHEA to estrone. I suggest that the combination of low DHEA and increased estrone cause the similarities in the brains of male homosexuals and the heterosexual females. A 1992 French study of homosexual men reported that estrone was 30-50% higher in all groups of HIV infected patients in addition to all also having low DHEAS (JAIDS 1992; 5: 841). It is now known that some homosexual men are vulnerable to the HIV and AIDS, while others have been exposed, but did not seroconvert (Science 1992; 257: 1032). The following chart demonstrates that some homosexual men have DHEA above the heterosexual population, while others produce very low levels (Biological Psychiatry 1973; 6: 31, after Fig. 3).
OK, SOMETHING DIFFERENT NOW: FOR DEPRESSION, AND SCHIZOPHRENIA:
http://corpus-callosum.blogspot.com/2006_02_01_archive.html

REPEAT OF NOTES FROM LAB DX WINTER 2009
DHEA
- = DEHYDROEPIANDOSTERONE
--steroid androgen precursor formed in adrenal cortex, testes and ovaries
--in general has a "tonic" effect on target tissues
--used as "anti-aging" hormone
--studies indicate anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity, anti-atherosclerotic, memory enhancing and immune system enhancing effects
--17-hydroxypregnenolone + 17,20 lyase-->DHEA
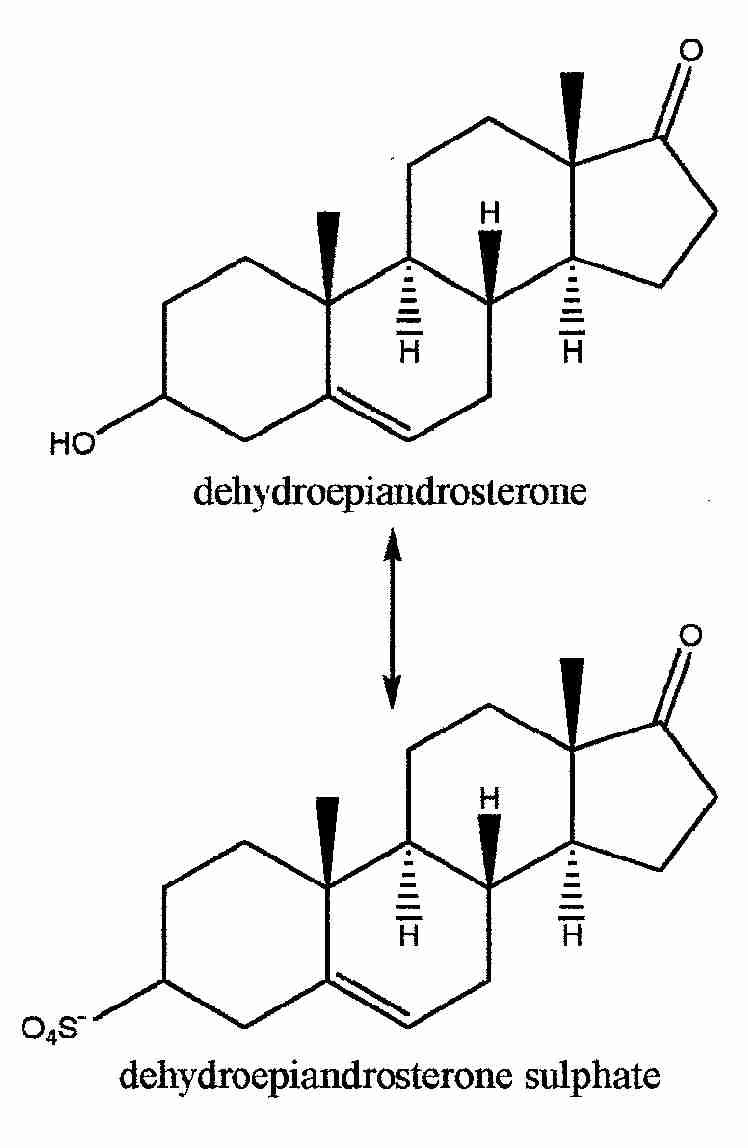
-- >90% of DHEA is conjugated with sulfate
--when conj to sulfate is DHEA-S, with 60% the biological activity of DHEA
--DHEA and DHEA-S are enzymatically interconvertible
--about 64-74% of DHEA-S --> DHEA (dynamic equilibrium)
--some evidence that DHEA levels are genetic
--other factors may influence but not well known
--DHEA ultijmate converted to testosterone, estrone, and estradiol
--peripheral conversion occurs in adipose after menopause (in men ???)
--levels very with age and gender, lower in childhood then spike before puberty (adrenarche), decrease substantial with age beginning around age 30 and down by 80% or more by age 75
--increased in: CAH, PCOS (T shift), adrenal cortical tumors, hirsutism, acute stress
--decreased in: adrenocortical failure, chronic stress (diverted to cortisol production), hypothyroidism
--saliva to plasma ratio: 0.001