tijd
in
puppet_djt
Карантин свободного мира

Франклин Рузвельт произнес знаменитую "карантинную речь" в октябре 1937. Не называя конкретные страны, он описывал эпидемию агрессии, которая катилась по миру, и призывал отгородить источники заразы.
"It seems to be unfortunately true that the epidemic of world lawlessness is spreading.
When an epidemic of physical disease starts to spread, the community approves and joins in a quarantine of the patients in order to protect the health of the community against the spread of the disease.
It is my determination to pursue a policy of peace. It is my determination to adopt every practicable measure to avoid involvement in war. It ought to be inconceivable that in this modern era, and in the face of experience, any nation could be so foolish and ruthless as to run the risk of plunging the whole world into war by invading and violating, in contravention of solemn treaties, the territory of other nations that have done them no real harm and are too weak to protect themselves adequately. Yet the peace of the world and the welfare and security of every nation, including our own, is today being threatened by that very thing."
https://millercenter.org/the-presidency/presidential-speeches/october-5-1937-quarantine-speech

Но остаться в стороне у США не получилось. Перешагнув через мировую войну, в марте 1947 Трумэн провозгласил "доктрину Трумэна", которая проводила линию от стратегии "сдерживания" Джорджа Кеннана до будущего плана Маршалла. Официальной политикой США становилась поддержка демократических стран от скатывания в тоталитаризм и от агрессии со стороны тоталитарных диктатур.
"I believe that it must be the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures.
I believe that we must assist free peoples to work out their own destinies in their own way.
I believe that our help should be primarily through economic and financial aid which is essential to economic stability and orderly political processes. <...>
The seeds of totalitarian regimes are nurtured by misery and want. They spread and grow in the evil soil of poverty and strife. They reach their full growth when the hope of a people for a better life has died. We must keep that hope alive.
The free peoples of the world look to us for support in maintaining their freedoms.
If we falter in our leadership, we may endanger the peace of the world -- and we shall surely endanger the welfare of our own nation."
https://avalon.law.yale.edu/20th_century/trudoc.asp
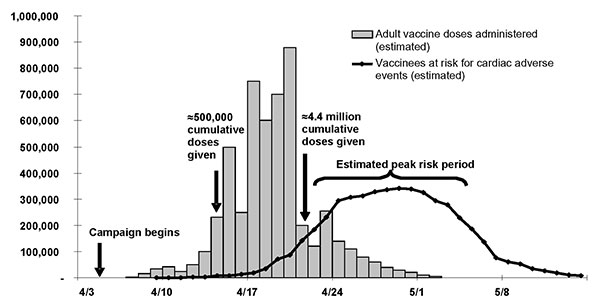
В том же месяце у Америки появилась возможность протестрировать способность демократического общества справляться с проблемами и заботиться о своих гражданах. Вспыхнувшую в Нью-Йорке эпидемию оспы удалось погасить эффективной кампанией добровольной вакцинации, за короткое время привив миллионы жителей города и погасив эпидемию в зародыше. Успеху способствовала слаженная работа местных властей (в частности доктора Израеля Вайнштейна), федеральных властей и частных компаний, а также сознательность обычных граждан.
With the threat of a major epidemic looming, city officials put together an emergency plan for mass inoculations. Newspapers and radio stations alerted the public to be immediately vaccinated. Some 650,000 doses of vaccine were immediately available, and another several hundred thousand units of vaccine was quickly gathered around the country and shipped to New York by the U.S. military. But that still wasn’t enough to inoculate the entire city; millions of doses were required. Time was running out.
New York Mayor William O’Dwyer called an emergency meeting of vaccine manufacturers, who began working around the clock to package and divert vaccine to the city. By this time, thousands of New Yorkers were lining up at hundreds of locations to be inoculated. At the White House, President Truman, who was planning a trip to New York, stood tall for the needle.
Some 500,000 people were vaccinated in the first two weeks, and by the end of April more than 6,350,000 had been immunized. New Yorkers, used to the wartime air-raid drills, had fully cooperated, even waiting in driving rain and lines that went around the block. There was no sense of panic among the population.
As Weinstein pointed out, “Never before had so many people in one city been vaccinated in such a short time and on such short notice,” averting “a major catastrophe…It is little short of remarkable that there were only 12 cases [and two deaths] in the entire outbreak.” Without the mass action, he declared, “there very likely would have been thousands of cases [of smallpox] and hundreds of deaths.”
“What happened in New York City was successful because of federal, state, and local communication, voluntary vaccinations, and a public information blitz-and that’s what’s needed in an any future potential pandemic, or epidemic,” asserts Judith W. Leavitt, professor of history of medicine at the University of Wisconsin.
https://www.thedailybeast.com/the-panic-of-1947
Победа над эпидемией оспы в Нью-Йорке в апреле 1947 до сих пор служит примером правильного просвещения граждан со стороны правительства во время кризиса: необходимо четко сообщать об опасности, предлагать универсальные правила для борьбы с ней и предоставлять автономию сознательным гражданам, чтобы они могли следовать этим правилам добровольно.
Today, the only way to slow the spread of the coronavirus is to win cooperation from the public. We know from history that this can be done. But only if any directives given to the public are understandable and fair and allow people some amount of autonomy. Until a vaccine is found, these three principles - clarity, fairness and autonomy - remain our best empirically proven approach. <...>
The health commissioner had the authority to forcibly hospitalize sick people, but he didn’t use it. Instead, he held daily news conferences and delivered clear, consistent, transparent messages to the public. The city handed out buttons, empowering people to “Be safe. Be sure. Get vaccinated.” They offered free vaccinations in every public and parochial school around the city. The mayor and even President Harry S. Truman got publicly vaccinated themselves.
In one month, more than 6 million New Yorkers got vaccinated - voluntarily. People waited hours for their turn. The city had braced itself for a possible 4,900 deaths, based on previous smallpox outbreaks; in the end, there were just 12 cases - and two deaths.
“What New York teaches us is, you inform and involve people in crafting solutions to the threat,” says medical anthropologist Monica Schoch-Spana at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. “You respect the public’s autonomy, and you give them the information they need.”
Last week, we got a glimpse of what this might look like at the national level - not in the United States but in Germany: “I firmly believe we will manage this task if really all citizens see it as their task,” Chancellor Angela Merkel said in a surprisingly honest address to the German people. “Nobody is expendable. Everybody counts. It requires effort by all of us. This is what an epidemic shows us.”
https://www.washingtonpost.com/opinions/2020/03/25/we-know-how-prepare-public-crisis-why-arent-we-doing-it/
В своей речи Трумэн говорил "No government is perfect. One of the chief virtues of a democracy, however, is that its defects are always visible and under democratic processes can be pointed out and corrected. " Он был знаком с этим из первых рук: Трумэн приобрел всенародную славу и был выбран в вице-президенты благодаря тому, что с марта 1941 возглавлял межпартийную сенатскую комиссию, которая осуществляла надзор за расходованием средств, выделенных на войну.
The Truman Committee proved to be one of the most successful investigative efforts ever mounted by the US government: an initial budget of $15,000 was expanded over three years to $360,000 to save an estimated $10-15 billion in military spending and thousands of lives of US servicemen. For comparison, the entire cost of the Manhattan Project was $2 billion, at the time. Chairing the committee helped Truman make a name for himself beyond his political machine origins and was a major factor in the decision to nominate him as vice president, which would propel him to the presidency after the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Truman_Committee
В 1945-1946 другая комиссия Конгресса расследовала обстоятельства японской атаки на Перл Харбор и каким образом эта атака оказалась сюрпризом для США. Результаты работы этой комиссии помогли принятию в 1947 закона National Security Act, который создал ЦРУ и Совет по национальной безопасности (NSC) при президенте.

Сравнимой по эффекту стала работа специальной комиссии по расследованию 9/11. Вывод о недостатке координации между различными федеральными службами привел к созданию администрацией Буша двух новых структур - директората национальной разведки (ODNI) и гигантского министерства национальной безопасности (DHS). Ныне обе структуры, обезглавленные Трампом, не смогли сыграть должной роли в борьбе с пандемием.
Во время 9/11 за борьбу с терроризмом в администрации Буша отвечал Ричард Кларк, глава отдела анти-терроризма в NSC. Давая показания комиссии, он покаялся перед американцами за то, что не смог уберечь их от теракта:
"I welcome these hearings because of the opportunity that they provide to the American people to better understand why the tragedy of 9/11 happened, and what we must do to prevent a reoccurrence. I also welcome the hearings because it is finally a forum where I can apologize to the loved ones of the victims of 9/11, to them who are here in the room, to those who are watching on television, your government failed you. Those entrusted with protecting you failed you. And I failed you. We tried hard, but that doesn't matter because we failed. And for that failure, I would ask, once all the facts are out, for your understanding and for your forgiveness."
https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB108016253085664479

В администрации Буша, как и в администрации Клинтона до него, существовала также должность ответственного по биозащите (Special Assistant to the President for Biodefense). Обама упразднил эту должность, но вынужден был к ней вернуться после эпидемии Эболы. В NSC был создан соответствующий отдел, ликвидированный Трампом и Болтоном в мае 2018.
Building on work done by similar iterations in the Bush administration, the NSC office was dedicated exclusively to be the smoke alarm to warn of the first sign of a fire before it becomes a blaze, Beth Cameron, who headed the office under Rice, tells TIME. It was designed to feed expertise and recommendations directly to key decision makers in the event of a global health crisis, when speed is essential. Focusing on detection and preparedness, it boosted international biosurveillance networks to track the next emerging disease.
It also measured the health capacities of several countries - their labs, emergency operation centers and epidemiology expertise, Cameron said. The unit’s job was to be ahead of the curve during an eventual pandemic, when everyone else - health agencies, hospitals, state and local governments - would be swallowed up by the demands of keeping up with a rapidly mounting number of cases.
The office continued to function during the first year and a half of the Trump Administration on the recommendation of White House Homeland Security Advisor Thomas P. Bossert, a vocal advocate for a comprehensive biodefense strategy against deadly pandemics. Bossert left when Bolton took charge in April 2018, and the health professional heading the team, Rear Adm. Timothy Ziemer, abruptly left his post in May.
At roughly the same time, the team was disbanded as part of Bolton’s broader effort to reorganize the NSC and reduce the body’s headcount of career officials from agencies detailed to the White House. Trump’s allies felt there were too many layers of bureaucracy and the large staff posed a heightened risk of leaks.
https://time.com/5806558/administration-officials-fight-criticism/

Буш упоминал про подготовку к пандемиям во время встречи с Путиным в Белом доме в сентябре 2005. Речь шла о выводах о подготовке правительства к катастрофам, которые предстояло сделать межпартийной комиссии по расследованию урагана Катрины.
Q: Last night you said that greater federal involvement and troops may be required in future disasters. Could you elaborate on that a little bit?
PRESIDENT BUSH: Yes. I don't want to prejudge the commission's -- what do they call it, the bipartisan commission that is set up in Congress. I don't want to prejudge their findings. But I do think they ought to seriously consider the fact that there are -- a storm, for example, of a certain category, which will require an overwhelming response by government that can only be provided by, say, the United States military through NORTHCOM, because of its ability to muster logistical -- logistics and supplies so quickly. And that's what I want Congress to consider. And I think it's very important that Congress consider this.
It's important for us to learn from the storm what could have been done better, for example, and apply that to other types of situations -- such as a pandemic. At the U.N. I talked about avian flu; we need to take it seriously. I talked to Vladimir about avian flu; I talked to other world leaders about the potential outbreak of avian flu: If avian flu were to hit this country, do we have the proper response mechanisms? Does the federal government have the authorities necessary to make certain decisions? And this storm will give us an opportunity to review all different types of circumstance to make sure that the President has the capacity to react. And that's what I was referring to. I wasn't drawing any conclusions; I was just suggesting that this be a matter of debate and discussion with the bipartisan commission that is going to be set up there, with Democrats and Republican senators and congressmen.
https://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2005/09/images/20050916-10_d-0588-515h.html
В докладе комиссии по Катрине говорилось:
"Not even the perfect bureaucratic storm of flaws and failures can wash away the fundamental governmental responsibility to protect public health and safety. <...>
It remains difficult to understand how government could respond so ineffectively to a disaster that was anticipated for years, and for which specific dire
warnings had been issued for days. This crisis was not only predictable, it was predicted.
If this is what happens when we have advance warning, we shudder to imagine the consequences when we do not. Four and a half years after 9/11, America is still not ready for prime time. <...>
Government failed because it did not learn from past experiences, or because lessons thought to be learned were somehow not implemented. If 9/11 was a failure of imagination, then Katrina was a failure of initiative. It was a failure of leadership."
https://www.npr.org/documents/2006/feb/katrina/house_report/katrina_report_full.pdf
Мы пока не знаем, удастся ли, подобно комиссиям прошлым лет, создать комиссию по расследованию провала администрации Трампа в спасении жизни американцев во время пандемии COVID-19 или комиссию по надзору над расходованием триллионов долларов, выделенных на экономический стимул в 2020.
Но уже явно видно, как система глобального порядка и демократического иммунитета, созданная 80 лет назад Рузвельтом и Трумэном, трещит по швам.

This is the first great crisis of the post-American world. The UN Security Council is nowhere to be seen, G20 is in the hands of the Crown Prince of Saudi Arabia and the White House has trumpeted America First and Everyone Alone for years. Only the virus is globalized.
- Carl Bildt (@carlbildt) April 1, 2020
The melting down of the President of the United States at these briefings marks the death of the US led liberal global order that was architected by FDR, built by Truman and protected from Eisenhower thru Obama. What comes next will be different from what has been.
- Steve Schmidt (@SteveSchmidtSES) April 6, 2020