Опять кацапы выспаться не дали
Тем не менее кацапы гонять меня гулять. Издевательства у них в ходу


Cимволичненько так в 9.22 6 дек. в Раю американском +11, а перед этим смотрел, что в Москве -11. Ну, чем не страна Антихриста. А что удивляться, если вспомнить ад коммуналок.
Убираю как-то мусор из-под дивана и тут кацапка «А там не надо убирать, я сама там уберу»
Из-за кацапов 7 дек. порвал лямку маски
8 дек. опять напряг по поводу экскурсии
14 декабря после скучнейшей прогулки сказала что если переедем на новую квартиру то она меня юридически может выгнать.
15 декабря ведьма кацапская опять издевается, отменила экскурсию.
20 декабря ведьма кацапская опять агрессивна потому что не любит Воскресенье
21 декабря опять кацапы выспаться не дали
15 июня ведьма кацапская опять издевается, накануне опять до 17.30
2 июля ведьма кацапская опять издевается с подоодеяльником (подоодеяльник это ерунда по сравнению с тем какие дела произошли за несколько дней до этого, а мы тогда в июне-июле не знали)
7 сентября ведьма кацапская опять издевается, мол почему отворачиваешься
8 сентября ведьма кацапская опять издевается, мол почему отворачиваешься
11 сентября ведьма кацапская опять издевается, мол почему отворачиваешься
18 октября ведьма кацапская опять издевается, мол почему отворачиваешься
8 ноября ведьма кацапская опять издевается, мол почему отворачиваешься
22 ноября ведьма кацапская опять издевается, мол почему отворачиваешься
13 декабря ведьма кацапская опять издевается, мол почему отворачиваешься
1 434 день президенства
Math Symbols List
List of all mathematical symbols and signs - meaning and examples.
- Basic math symbols
- Geometry symbols
- Algebra symbols
- Probability & statistics symbols
- Set theory symbols
- Logic symbols
- Calculus & analysis symbols
- Number symbols
- Greek symbols
- Roman numerals
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExample=equals signequality5 = 2+3
5 is equal to 2+3≠not equal signinequality5 ≠ 4
5 is not equal to 4≈approximately equalapproximationsin(0.01) ≈ 0.01,
x ≈ y means x is approximately equal to y>strict inequalitygreater than5 > 4
5 is greater than 44 is less than 5≥inequalitygreater than or equal to5 ≥ 4,
x ≥ y means x is greater than or equal to y≤inequalityless than or equal to4 ≤ 5,
x ≤ y means x is less than or equal to y( )parenthesescalculate expression inside first2 × (3+5) = 16[ ]bracketscalculate expression inside first[(1+2)×(1+5)] = 18+plus signaddition1 + 1 = 2−minus signsubtraction2 − 1 = 1±plus - minusboth plus and minus operations3 ± 5 = 8 or -2±minus - plusboth minus and plus operations3 ∓ 5 = -2 or 8*asteriskmultiplication2 * 3 = 6×times signmultiplication2 × 3 = 6⋅multiplication dotmultiplication2 ⋅ 3 = 6÷division sign / obelusdivision6 ÷ 2 = 3/division slashdivision6 / 2 = 3-horizontal linedivision / fraction
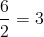
modmoduloremainder calculation7 mod 2 = 1.perioddecimal point, decimal separator2.56 = 2+56/100abpowerexponent23 = 8a^bcaretexponent2 ^ 3 = 8√asquare root
√a ⋅ √a = a
√9 = ±33√acube root3√a ⋅ 3√a ⋅ 3√a = a3√8 = 24√afourth root4√a ⋅ 4√a ⋅ 4√a ⋅ 4√a = a4√16 = ±2n√an-th root (radical) for n=3, n√8 = 2%percent1% = 1/10010% × 30 = 3‰per-mille1‰ = 1/1000 = 0.1%10‰ × 30 = 0.3ppmper-million1ppm = 1/100000010ppm × 30 = 0.0003ppbper-billion1ppb = 1/100000000010ppb × 30 = 3×10-7pptper-trillion1ppt = 10-1210ppt × 30 = 3×10-10
Geometry symbols
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExample∠angleformed by two rays∠ABC = 30°
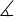
measured angle
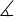
ABC = 30°
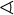
spherical angle
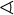
AOB = 30°∟right angle= 90°α = 90°°degree1 turn = 360°α = 60°degdegree1 turn = 360degα = 60deg′primearcminute, 1° = 60′α = 60°59′″double primearcsecond, 1′ = 60″α = 60°59′59″
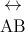
lineinfinite line ABline segmentline from point A to point B
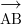
rayline that start from point A
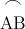
arcarc from point A to point B
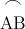
= 60°⊥perpendicularperpendicular lines (90° angle)AC ⊥ BC∥parallelparallel linesAB ∥ CD≅congruent toequivalence of geometric shapes and size∆ABC≅ ∆XYZ~similaritysame shapes, not same size∆ABC~ ∆XYZΔtriangletriangle shapeΔABC≅ ΔBCD|x-y|distancedistance between points x and y| x-y | = 5πpi constantπ = 3.141592654...
is the ratio between the circumference and diameter of a circle
c = π⋅d = 2⋅π⋅rradradiansradians angle unit360° = 2π radcradiansradians angle unit360° = 2π cgradgradians / gonsgrads angle unit360° = 400 gradggradians / gonsgrads angle unit360° = 400 g
Algebra symbols
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExamplexx variableunknown value to findwhen 2x = 4, then x = 2≡equivalenceidentical to ≜equal by definitionequal by definition :=equal by definitionequal by definition ~approximately equalweak approximation11 ~ 10≈approximately equalapproximationsin(0.01) ≈ 0.01∝proportional toproportional to
y ∝ x when y = kx, kconstant
∞lemniscateinfinity symbol ≪much less thanmuch less than1 ≪ 1000000≫much greater thanmuch greater than1000000 ≫ 1( )parenthesescalculate expression inside first2 * (3+5) = 16[ ]bracketscalculate expression inside first[(1+2)*(1+5)] = 18{ }bracesset ⌊x⌋floor bracketsrounds number to lower integer⌊4.3⌋ = 4⌈x⌉ceiling bracketsrounds number to upper integer⌈4.3⌉ = 5x!exclamation markfactorial4! = 1*2*3*4 = 24| x |vertical barsabsolute value| -5 | = 5f (x)function of xmaps values of x to f(x)f (x) = 3x+5(f ∘ g)function composition(f ∘ g) (x) = f (g(x))f (x)=3x,g(x)=x-1 ⇒(f ∘ g)(x)=3(x-1)(a,b)open interval(a,b) = {x | a < x < b}x∈ (2,6)[a,b]closed interval[a,b] = {x | a ≤ x ≤ b}x ∈ [2,6]∆deltachange / difference∆t = t1 - t0∆discriminantΔ = b2 - 4ac ∑sigmasummation - sum of all values in range of series∑ xi= x1+x2+...+xn∑∑sigmadouble summation
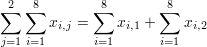
∏capital piproduct - product of all values in range of series∏ xi=x1∙x2∙...∙xnee constant / Euler's numbere = 2.718281828...e = lim (1+1/x)x , x→∞γEuler-Mascheroni constantγ = 0.5772156649... φgolden ratiogolden ratio constant πpi constantπ = 3.141592654...
is the ratio between the circumference and diameter of a circle
c = π⋅d = 2⋅π⋅r
Linear Algebra Symbols
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExample·dotscalar producta · b×crossvector producta × bA⊗Btensor producttensor product of A and BA ⊗ B
inner product [ ]bracketsmatrix of numbers ( )parenthesesmatrix of numbers | A |determinantdeterminant of matrix A det(A)determinantdeterminant of matrix A || x ||double vertical barsnorm ATtransposematrix transpose(AT)ij = (A)jiA†Hermitian matrixmatrix conjugate transpose(A†)ij = (A)jiA*Hermitian matrixmatrix conjugate transpose(A*)ij = (A)jiA -1inverse matrixA A-1 = I rank(A)matrix rankrank of matrix Arank(A) = 3dim(U)dimensiondimension of matrix Adim(U) = 3
Probability and statistics symbols
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExampleP(A)probability functionprobability of event AP(A) = 0.5P(A ⋂ B)probability of events intersectionprobability that of events A and BP(A⋂B) = 0.5P(A ⋃ B)probability of events unionprobability that of events A or BP(A⋃B) = 0.5P(A | B)conditional probability functionprobability of event A given event B occuredP(A | B) = 0.3f (x)probability density function (pdf)P(a ≤ x ≤ b) = ∫ f (x) dx F(x)cumulative distribution function (cdf)F(x) = P(X≤ x) μpopulation meanmean of population valuesμ = 10E(X)expectation valueexpected value of random variable XE(X) = 10E(X | Y)conditional expectationexpected value of random variable X given YE(X | Y=2) = 5var(X)variancevariance of random variable Xvar(X) = 4σ2variancevariance of population valuesσ2 = 4std(X)standard deviationstandard deviation of random variable Xstd(X) = 2σXstandard deviationstandard deviation value of random variable XσX = 2
medianmiddle value of random variable x
cov(X,Y)covariancecovariance of random variables X and Ycov(X,Y) = 4corr(X,Y)correlationcorrelation of random variables X and Ycorr(X,Y) = 0.6ρX,Ycorrelationcorrelation of random variables X and YρX,Y = 0.6∑summationsummation - sum of all values in range of series
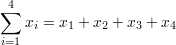
∑∑double summationdouble summation
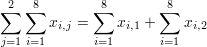
Momodevalue that occurs most frequently in population MRmid-rangeMR = (xmax+xmin)/2 Mdsample medianhalf the population is below this value Q1lower / first quartile25% of population are below this value Q2median / second quartile50% of population are below this value = median of samples Q3upper / third quartile75% of population are below this value xsample meanaverage / arithmetic meanx = (2+5+9) / 3 = 5.333s 2sample variancepopulation samples variance estimators 2 = 4ssample standard deviationpopulation samples standard deviation estimators = 2zxstandard scorezx = (x-x) / sx X ~distribution of Xdistribution of random variable XX ~ N(0,3)N(μ,σ2)normal distributiongaussian distributionX ~ N(0,3)U(a,b)uniform distributionequal probability in range a,b X ~ U(0,3)exp(λ)exponential distributionf (x) = λe-λx , x≥0 gamma(c, λ)gamma distributionf (x) = λ c xc-1e-λx / Γ(c), x≥0 χ 2(k)chi-square distributionf (x) = xk/2-1e-x/2 / ( 2k/2 Γ(k/2) ) F (k1, k2)F distribution Bin(n,p)binomial distributionf (k) = nCk pk(1-p)n-k Poisson(λ)Poisson distributionf (k) = λke-λ / k! Geom(p)geometric distributionf (k) = p(1-p) k HG(N,K,n)hyper-geometric distribution Bern(p)Bernoulli distribution
Combinatorics Symbols
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExamplen!factorialn! = 1⋅2⋅3⋅...⋅n5! = 1⋅2⋅3⋅4⋅5 = 120nPkpermutation
5P3 = 5! / (5-3)! = 60nCk
combination
5C3 = 5!/[3!(5-3)!]=10
Set theory symbols
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExample{ }seta collection of elementsA = {3,7,9,14},
B = {9,14,28}A ∩ Bintersectionobjects that belong to set A and set BA ∩ B = {9,14}A ∪ Bunionobjects that belong to set A or set BA ∪ B = {3,7,9,14,28}A ⊆ BsubsetA is a subset of B. set A is included in set B.{9,14,28} ⊆ {9,14,28}A ⊂ Bproper subset / strict subsetA is a subset of B, but A is not equal to B.{9,14} ⊂ {9,14,28}A ⊄ Bnot subsetset A is not a subset of set B{9,66} ⊄ {9,14,28}A ⊇ BsupersetA is a superset of B. set A includes set B{9,14,28} ⊇ {9,14,28}A ⊃ Bproper superset / strict supersetA is a superset of B, but B is not equal to A.{9,14,28} ⊃ {9,14}A ⊅ Bnot supersetset A is not a superset of set B{9,14,28} ⊅ {9,66}2Apower setall subsets of A
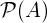
power setall subsets of A A = Bequalityboth sets have the same membersA={3,9,14},
B={3,9,14},
A=BAccomplementall the objects that do not belong to set A A \ Brelative complementobjects that belong to A and not to BA = {3,9,14},
B = {1,2,3},
A-B = {9,14}A - Brelative complementobjects that belong to A and not to BA = {3,9,14},
B = {1,2,3},
A-B = {9,14}A ∆ Bsymmetric differenceobjects that belong to A or B but not to their intersectionA = {3,9,14},
B = {1,2,3},
A ∆ B = {1,2,9,14}A ⊖ Bsymmetric differenceobjects that belong to A or B but not to their intersectionA = {3,9,14},
B = {1,2,3},
A ⊖ B = {1,2,9,14}a∈Aelement of,
belongs toset membershipA={3,9,14}, 3 ∈ Ax∉Anot element ofno set membershipA={3,9,14}, 1 ∉ A(a,b)ordered paircollection of 2 elements A×Bcartesian productset of all ordered pairs from A and BA×B = {(a,b)|a∈A , b∈B}|A|cardinalitythe number of elements of set AA={3,9,14}, |A|=3#Acardinalitythe number of elements of set AA={3,9,14}, #A=3|vertical barsuch thatA={x|3
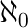
aleph-nullinfinite cardinality of natural numbers set
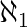
aleph-onecardinality of countable ordinal numbers set Øempty setØ = { }C = {Ø}
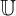
universal setset of all possible values
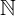
0natural numbers / whole numbers set (with zero)
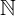
0 = {0,1,2,3,4,...}0 ∈
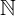
0
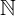
1natural numbers / whole numbers set (without zero)
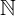
1 = {1,2,3,4,5,...}6 ∈
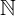
1
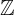
integer numbers set
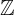
= {...-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,...}-6 ∈
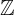
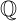
rational numbers set
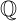
= {x | x=a/b, a,b∈
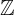
}2/6 ∈
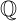
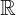
real numbers set
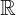
= {x | -∞ < x <∞}6.343434∈
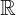
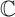
complex numbers set
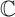
= {z | z=a+bi, -∞
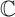
Logic symbols
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExample⋅andandx ⋅ y^caret / circumflexandx ^ y&ersandandx & y+plusorx + y∨reversed caretorx ∨ y|vertical lineorx | yx'single quotenot - negationx'xbarnot - negationx¬notnot - negation¬ x!exclamation marknot - negation! x⊕circled plus / oplusexclusive or - xorx ⊕ y~tildenegation~ x⇒implies ⇔equivalentif and only if (iff) ↔equivalentif and only if (iff) ∀for all ∃there exists ∄there does not exists ∴therefore ∵because / since
Calculus & analysis symbols
SymbolSymbol NameMeaning / definitionExample
limitlimit value of a function εepsilonrepresents a very small number, near zeroε → 0ee constant / Euler's numbere = 2.718281828...e = lim (1+1/x)x , x→∞y 'derivativederivative - Lagrange's notation(3x3)' = 9x2y ''second derivativederivative of derivative(3x3)'' = 18xy(n)nth derivativen times derivation(3x3)(3) = 18
derivativederivative - Leibniz's notationd(3x3)/dx = 9x2
second derivativederivative of derivatived2(3x3)/dx2 = 18x
nth derivativen times derivation
time derivativederivative by time - Newton's notation
time second derivativederivative of derivative Dx yderivativederivative - Euler's notation Dx2ysecond derivativederivative of derivative
partial derivative ∂(x2+y2)/∂x= 2x∫integralopposite to derivation∫ f(x)dx∫∫double integralintegration of function of 2 variables∫∫ f(x,y)dxdy∫∫∫triple integralintegration of function of 3 variables∫∫∫ f(x,y,z)dxdydz∮closed contour / line integral ∯closed surface integral ∰closed volume integral [a,b]closed interval[a,b] = {x | a ≤ x ≤ b} (a,b)open interval(a,b) = {x | a < x < b} iimaginary uniti ≡ √-1z = 3 + 2iz*complex conjugatez = a+bi → z*=a-biz* = 3 - 2izcomplex conjugatez = a+bi → z = a-biz = 3 - 2iRe(z)real part of a complex numberz = a+bi → Re(z)=aRe(3 - 2i) = 3Im(z)imaginary part of a complex numberz = a+bi → Im(z)=bIm(3 - 2i) = -2| z |absolute value/magnitude of a complex number|z| = |a+bi| = √(a2+b2)|3 - 2i| = √13arg(z)argument of a complex numberThe angle of the radius in the complex planearg(3 + 2i) = 33.7°∇nabla / delgradient / divergence operator∇f (x,y,z)
vector
unit vector x * yconvolutiony(t) = x(t) * h(t)
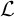
Laplace transformF(s) =
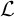
{f (t)}
Fourier transformX(ω) =
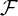
{f (t)} δdelta function ∞lemniscateinfinity symbol