Making America Great Again (for The Rich)
America is Regressing into a Developing Nation for Most People
A new book by economist Peter Temin finds that the U.S. is no longer one country, but dividing into two separate economic and political worlds
You’ve probably heard the news that the celebrated post-WW II beating heart of America known as the middle class has gone from “burdened,” to “squeezed” to “dying.” But you might have heard less about what exactly is emerging in its place.
In a new book, The Vanishing Middle Class: Prejudice and Power in a Dual Economy, Peter Temin, Professor Emeritus of Economics at MIT, draws a portrait of the new reality in a way that is frighteningly, indelibly clear: America is not one country anymore. It is becoming two, each with vastly different resources, expectations, and fates.
Two roads diverged
In one of these countries live members of what Temin calls the “FTE sector” (named for finance, technology, and electronics, the industries which largely support its growth). These are the 20 percent of Americans who enjoy college educations, have good jobs, and sleep soundly knowing that they have not only enough money to meet life’s challenges, but also social networks to bolster their success. They grow up with parents who read books to them, tutors to help with homework, and plenty of stimulating things to do and places to go. They travel in planes and drive new cars. The citizens of this country see economic growth all around them and exciting possibilities for the future. They make plans, influence policies, and count themselves as lucky to be Americans.
The FTE citizens rarely visit the country where the other 80 percent of Americans live: the low-wage sector. Here, the world of possibility is shrinking, often dramatically. People are burdened with debt and anxious about their insecure jobs if they have a job at all. Many of them are getting sicker and dying younger than they used to. They get around by crumbling public transport and cars they have trouble paying for. Family life is uncertain here; people often don’t partner for the long-term even when they have children. If they go to college, they finance it by going heavily into debt. They are not thinking about the future; they are focused on surviving the present. The world in which they reside is very different from the one they were taught to believe in. While members of the first country act, these people are acted upon.
The two sectors, notes Temin, have entirely distinct financial systems, residential situations, and educational opportunities. Quite different things happen when they get sick, or when they interact with the law. They move independently of each other. Only one path exists by which the citizens of the low-wage country can enter the affluent one, and that path is fraught with obstacles. Most have no way out.
The richest large economy in the world, says Temin, is coming to have an economic and political structure more like a developing nation. We have entered a phase of regression, and one of the easiest ways to see it is in our infrastructure: our roads and bridges look more like those in Thailand or Venezuela than the Netherlands or Japan. But it goes far deeper than that, which is why Temin uses a famous economic model created to understand developing nations to describe how far inequality has progressed in the United States. The model is the work of West Indian economist W. Arthur Lewis, the only person of African descent to win a Nobel Prize in economics. For the first time, this model is applied with systematic precision to the U.S.
The result is profoundly disturbing.
In the Lewis model of a dual economy, much of the low-wage sector has little influence over public policy. Check. The high-income sector will keep wages down in the other sector to provide cheap labor for its businesses. Check. Social control is used to keep the low-wage sector from challenging the policies favored by the high-income sector. Mass incarceration - check. The primary goal of the richest members of the high-income sector is to lower taxes. Check. Social and economic mobility is low. Check.
In the developing countries Lewis studied, people try to move from the low-wage sector to the affluent sector by transplanting from rural areas to the city to get a job. Occasionally it works; often it doesn’t. Temin says that today in the U.S., the ticket out is education, which is difficult for two reasons: you have to spend money over a long period of time, and the FTE sector is making those expenditures more and more costly by defunding public schools and making policies that increase student debt burdens.
Getting a good education, Temin observes, isn’t just about a college degree. It has to begin in early childhood, and you need parents who can afford to spend time and resources all along the long journey. If you aspire to college and your family can’t make transfers of money to you on the way, well, good luck to you. Even with a diploma, you will likely find that high-paying jobs come from networks of peers and relatives. Social capital, as well as economic capital, is critical, but because of America’s long history of racism and the obstacles it has created for accumulating both kinds of capital, black graduates often can only find jobs in education, social work, and government instead of higher-paying professional jobs like technology or finance- something most white people are not really aware of. Women are also held back by a long history of sexism and the burdens - made increasingly heavy - of making greater contributions to the unpaid care economy and lack of access to crucial healthcare.
How did we get this way?
What happened to America’s middle class, which rose triumphantly in the post-World War II years, buoyed by the GI bill, the victories of labor unions, and programs that gave the great mass of workers and their families health and pension benefits that provided security?
The dual economy didn’t happen overnight, says Temin. The story started just a couple of years after the ’67 Summer of Love. Around 1970, the productivity of workers began to get divided from their wages. Corporate attorney and later Supreme Court Justice Lewis Powell galvanized the business community to lobby vigorously for its interests. Johnson’s War on Poverty was replaced by Nixon’s War on Drugs, which sectioned off many members of the low-wage sector, disproportionately black, into prisons. Politicians increasingly influenced by the FTE sector turned from public-spirited universalism to free-market individualism. As money-driven politics accelerated (a phenomenon explained by the Investment Theory of Politics, as Temin explains), leaders of the FTE sector became increasingly emboldened to ignore the needs of members of the low-wage sector, or even to actively work against them.
America’s underlying racism has a continuing distorting impact. A majority of the low-wage sector is white, with blacks and Latinos making up the other part, but politicians learned to talk as if the low-wage sector is mostly black because it allowed them to appeal to racial prejudice, which is useful in maintaining support for the structure of the dual economy - and hurting everyone in the low-wage sector. Temin notes that “the desire to preserve the inferior status of blacks has motivated policies against all members of the low-wage sector.”
Temin points out that the presidential race of 2016 both revealed and amplified the anger of the low-wage sector at this increasing imbalance. Low-wage whites who had been largely invisible in public policy until recently came out of their quiet despair to be heard. Unfortunately, present trends are not only continuing, but also accelerating their problems, freezing the dual economy into place.
What can we do?
We’ve been digging ourselves into a hole for over forty years, but Temin says that we know how to stop digging. If we spent more on domestic rather than military activities, then the middle class would not vanish as quickly. The effects of technological change and globalization could be altered by political actions. We could restore and expand education, shifting resources from policies like mass incarceration to improving the human and social capital of all Americans. We could upgrade infrastructure, forgive mortgage and educational debt in the low-wage sector, reject the notion that private entities should replace democratic government in directing society, and focus on embracing an integrated American population. We could tax not only the income of the rich, but also their capital.
The cost of not doing these things, Temin warns, is incalculably high, and even the rich will end up paying for it:
“Look at the movie, Hidden Figures: It recounts a very dramatic story about three African American women condemned to have a life of not being paid very well teaching in black colleges, and yet their fates changed when they were tapped by NASA to contribute to space exploration. Today we are losing the ability to find people like that. We have a structure that predetermines winners and losers. We are not getting the benefits of all the people who could contribute to the growth of the economy, to advances in medicine or science which could improve the quality of life for everyone - including some of the rich people.”
Along with Thomas Piketty, whose Capital in the Twenty-First Century examines historical and modern inequality, Temin’s book has provided a giant red flag, illustrating a trajectory that will continue to accelerate as long as the 20 percent in the FTE sector are permitted to operate a country within America’s borders solely for themselves at the expense of the majority. Without a robust middle class, America is not only reverting to developing-country status, it is increasingly ripe for serious social turmoil that has not been seen in generations.
A dual economy has separated America from the idea of what most of us thought the country was meant to be.
America is Regressing into a Developing Nation for Most People
The Rich Are Living Longer and Taking More From Taxpayers
Social Security is becoming a much better deal for the wealthy.
We’re living longer and longer. Well, some of us.
Age 100 is now an imaginable goal for young people around the world with good health care. The average woman in Japan is already living to 87. Yet many Americans are dying younger and younger. Based on the latest year of data, the Society of Actuaries last fall dropped its life expectancy estimates for 65-year-olds in the U.S. by six months. The health of middle-aged non-Hispanic white Americans is deteriorating fastest.
The result of these trends, according to a new study, is a widening gap between wealthier and poorer Americans. The richest people in the U.S. aren’t just getting several years of extra life, they’re also reaping a financial reward for their longevity - courtesy of the U.S. taxpayer. These trends will be crucial as the new administration and Congress consider any changes to Social Security, Medicare, and other programs. Even tweaks to these programs, from the retirement age to benefit formulas, could affect the rich and poor very differently.
The researchers, a group of 13 prominent economists and health policy experts 1 , tried to figure out how long Americans can expect to live based on their income, focusing on earnings in midcareer, from 41 to 51, and using Social Security data.
The results are stark. In 1980, a 50-year-old man in the wealthiest fifth of the income distribution could expect to live five years longer than a 50-year-old man in the lowest-income group. By 2010, the gap between them had jumped to 12.7 years.
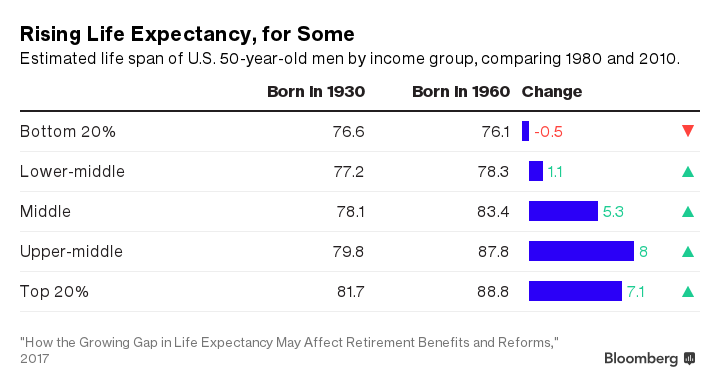
In other words, the poorest fifth of 50-year-old American men can now expect to live just past 76, six months shy of the previous generation. The richest 50-year-olds should make it almost to 89, seven years longer than their parents' generation.
The study focuses on men because the researchers considered the data on women less reliable. Women's move into the workforce over the past 40 years can skew the numbers, for example, because earlier generations of women sometimes had low reported earnings while having a relatively high socioeconomic status. While the researchers weren't prepared to produce specific estimates for women, though, they were confident that women experienced a “similar if not larger change over time” compared with men, citing a previous analysis.
One important result of this 13-year life expectancy gap: Social Security and other government programs, such as Medicare, are becoming a much better deal for well-off Americans.
Three decades ago, the richest and poorest retirees could expect about the same amount of benefits out of government programs. The richest generally got larger Social Security payouts, both by qualifying for higher checks and by living longer. The poorest got more out of other programs, such as Medicaid and Social Security disability insurance. Medicare offered about the same benefits to rich and poor.
The math has shifted dramatically. As wealthier people live longer, they can expect to collect much more from Social Security over their lifetimes than the poor. This chart shows the growing gap, based on the present value of benefits to a 50-year-old looking ahead, and using 2009 U.S. dollars to account for inflation.
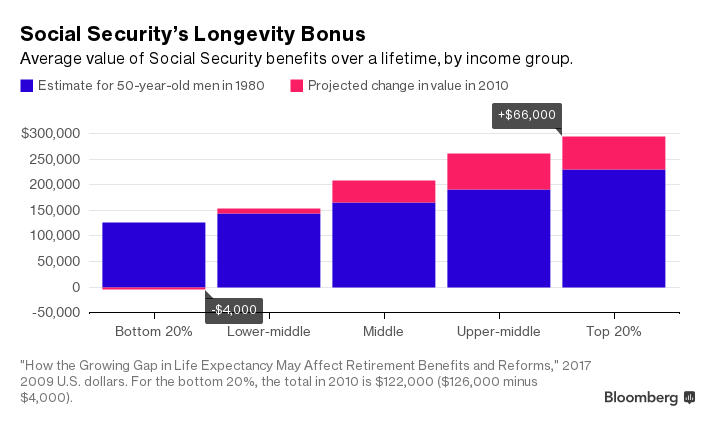
In 1980, a wealthier 50-year-old could expect to collect $103,000 more than a poor American. Thirty years later, the gap was $173,000. “These results suggest that Social Security is becoming significantly less progressive over time due to the widening gap in life expectancy,” the researchers write.
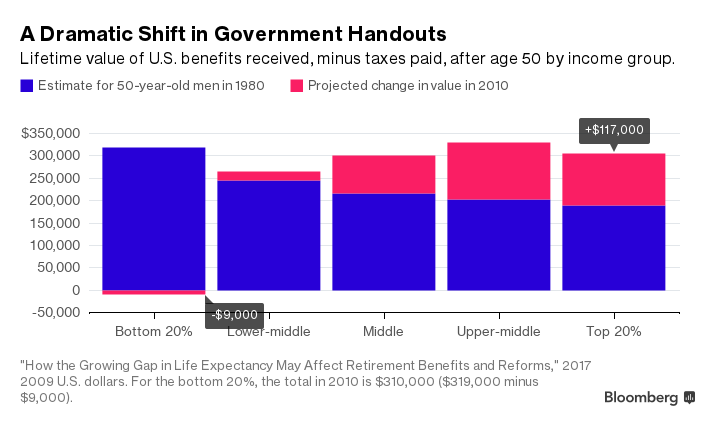
The U.S. retirement system looks more even-handed if you include in the analysis all government benefits received and all taxes paid by Americans after age 50. Still, longer lives are giving the rich and upper middle class a big financial boost, especially through Medicare and Social Security, even as the poorest Americans lose ground.
There are several theories on why the health of wide swaths of the U.S. is getting so much worse while the wealthy are thriving and living so much longer. Some cite rising levels of substance abuse, obesity, and suicide. Others point to the ways economic inequality drive health inequality. The cost of good health care has skyrocketed, even for people who are technically covered by insurance.
Your expected life span is obviously a factor when planning and saving for retirement. The longer you live, the more valuable Social Security is as a safety net to supplement your savings. Life expectancy trends also affect the long-term finances of entitlement programs such as Social Security.
For the moment, the most pressing question is why so many Americans are dying young, and how to stop it.
The Rich Are Living Longer and Taking More From Taxpayers
A new book by economist Peter Temin finds that the U.S. is no longer one country, but dividing into two separate economic and political worlds
You’ve probably heard the news that the celebrated post-WW II beating heart of America known as the middle class has gone from “burdened,” to “squeezed” to “dying.” But you might have heard less about what exactly is emerging in its place.
In a new book, The Vanishing Middle Class: Prejudice and Power in a Dual Economy, Peter Temin, Professor Emeritus of Economics at MIT, draws a portrait of the new reality in a way that is frighteningly, indelibly clear: America is not one country anymore. It is becoming two, each with vastly different resources, expectations, and fates.
Two roads diverged
In one of these countries live members of what Temin calls the “FTE sector” (named for finance, technology, and electronics, the industries which largely support its growth). These are the 20 percent of Americans who enjoy college educations, have good jobs, and sleep soundly knowing that they have not only enough money to meet life’s challenges, but also social networks to bolster their success. They grow up with parents who read books to them, tutors to help with homework, and plenty of stimulating things to do and places to go. They travel in planes and drive new cars. The citizens of this country see economic growth all around them and exciting possibilities for the future. They make plans, influence policies, and count themselves as lucky to be Americans.
The FTE citizens rarely visit the country where the other 80 percent of Americans live: the low-wage sector. Here, the world of possibility is shrinking, often dramatically. People are burdened with debt and anxious about their insecure jobs if they have a job at all. Many of them are getting sicker and dying younger than they used to. They get around by crumbling public transport and cars they have trouble paying for. Family life is uncertain here; people often don’t partner for the long-term even when they have children. If they go to college, they finance it by going heavily into debt. They are not thinking about the future; they are focused on surviving the present. The world in which they reside is very different from the one they were taught to believe in. While members of the first country act, these people are acted upon.
The two sectors, notes Temin, have entirely distinct financial systems, residential situations, and educational opportunities. Quite different things happen when they get sick, or when they interact with the law. They move independently of each other. Only one path exists by which the citizens of the low-wage country can enter the affluent one, and that path is fraught with obstacles. Most have no way out.
The richest large economy in the world, says Temin, is coming to have an economic and political structure more like a developing nation. We have entered a phase of regression, and one of the easiest ways to see it is in our infrastructure: our roads and bridges look more like those in Thailand or Venezuela than the Netherlands or Japan. But it goes far deeper than that, which is why Temin uses a famous economic model created to understand developing nations to describe how far inequality has progressed in the United States. The model is the work of West Indian economist W. Arthur Lewis, the only person of African descent to win a Nobel Prize in economics. For the first time, this model is applied with systematic precision to the U.S.
The result is profoundly disturbing.
In the Lewis model of a dual economy, much of the low-wage sector has little influence over public policy. Check. The high-income sector will keep wages down in the other sector to provide cheap labor for its businesses. Check. Social control is used to keep the low-wage sector from challenging the policies favored by the high-income sector. Mass incarceration - check. The primary goal of the richest members of the high-income sector is to lower taxes. Check. Social and economic mobility is low. Check.
In the developing countries Lewis studied, people try to move from the low-wage sector to the affluent sector by transplanting from rural areas to the city to get a job. Occasionally it works; often it doesn’t. Temin says that today in the U.S., the ticket out is education, which is difficult for two reasons: you have to spend money over a long period of time, and the FTE sector is making those expenditures more and more costly by defunding public schools and making policies that increase student debt burdens.
Getting a good education, Temin observes, isn’t just about a college degree. It has to begin in early childhood, and you need parents who can afford to spend time and resources all along the long journey. If you aspire to college and your family can’t make transfers of money to you on the way, well, good luck to you. Even with a diploma, you will likely find that high-paying jobs come from networks of peers and relatives. Social capital, as well as economic capital, is critical, but because of America’s long history of racism and the obstacles it has created for accumulating both kinds of capital, black graduates often can only find jobs in education, social work, and government instead of higher-paying professional jobs like technology or finance- something most white people are not really aware of. Women are also held back by a long history of sexism and the burdens - made increasingly heavy - of making greater contributions to the unpaid care economy and lack of access to crucial healthcare.
How did we get this way?
What happened to America’s middle class, which rose triumphantly in the post-World War II years, buoyed by the GI bill, the victories of labor unions, and programs that gave the great mass of workers and their families health and pension benefits that provided security?
The dual economy didn’t happen overnight, says Temin. The story started just a couple of years after the ’67 Summer of Love. Around 1970, the productivity of workers began to get divided from their wages. Corporate attorney and later Supreme Court Justice Lewis Powell galvanized the business community to lobby vigorously for its interests. Johnson’s War on Poverty was replaced by Nixon’s War on Drugs, which sectioned off many members of the low-wage sector, disproportionately black, into prisons. Politicians increasingly influenced by the FTE sector turned from public-spirited universalism to free-market individualism. As money-driven politics accelerated (a phenomenon explained by the Investment Theory of Politics, as Temin explains), leaders of the FTE sector became increasingly emboldened to ignore the needs of members of the low-wage sector, or even to actively work against them.
America’s underlying racism has a continuing distorting impact. A majority of the low-wage sector is white, with blacks and Latinos making up the other part, but politicians learned to talk as if the low-wage sector is mostly black because it allowed them to appeal to racial prejudice, which is useful in maintaining support for the structure of the dual economy - and hurting everyone in the low-wage sector. Temin notes that “the desire to preserve the inferior status of blacks has motivated policies against all members of the low-wage sector.”
Temin points out that the presidential race of 2016 both revealed and amplified the anger of the low-wage sector at this increasing imbalance. Low-wage whites who had been largely invisible in public policy until recently came out of their quiet despair to be heard. Unfortunately, present trends are not only continuing, but also accelerating their problems, freezing the dual economy into place.
What can we do?
We’ve been digging ourselves into a hole for over forty years, but Temin says that we know how to stop digging. If we spent more on domestic rather than military activities, then the middle class would not vanish as quickly. The effects of technological change and globalization could be altered by political actions. We could restore and expand education, shifting resources from policies like mass incarceration to improving the human and social capital of all Americans. We could upgrade infrastructure, forgive mortgage and educational debt in the low-wage sector, reject the notion that private entities should replace democratic government in directing society, and focus on embracing an integrated American population. We could tax not only the income of the rich, but also their capital.
The cost of not doing these things, Temin warns, is incalculably high, and even the rich will end up paying for it:
“Look at the movie, Hidden Figures: It recounts a very dramatic story about three African American women condemned to have a life of not being paid very well teaching in black colleges, and yet their fates changed when they were tapped by NASA to contribute to space exploration. Today we are losing the ability to find people like that. We have a structure that predetermines winners and losers. We are not getting the benefits of all the people who could contribute to the growth of the economy, to advances in medicine or science which could improve the quality of life for everyone - including some of the rich people.”
Along with Thomas Piketty, whose Capital in the Twenty-First Century examines historical and modern inequality, Temin’s book has provided a giant red flag, illustrating a trajectory that will continue to accelerate as long as the 20 percent in the FTE sector are permitted to operate a country within America’s borders solely for themselves at the expense of the majority. Without a robust middle class, America is not only reverting to developing-country status, it is increasingly ripe for serious social turmoil that has not been seen in generations.
A dual economy has separated America from the idea of what most of us thought the country was meant to be.
America is Regressing into a Developing Nation for Most People
The Rich Are Living Longer and Taking More From Taxpayers
Social Security is becoming a much better deal for the wealthy.
We’re living longer and longer. Well, some of us.
Age 100 is now an imaginable goal for young people around the world with good health care. The average woman in Japan is already living to 87. Yet many Americans are dying younger and younger. Based on the latest year of data, the Society of Actuaries last fall dropped its life expectancy estimates for 65-year-olds in the U.S. by six months. The health of middle-aged non-Hispanic white Americans is deteriorating fastest.
The result of these trends, according to a new study, is a widening gap between wealthier and poorer Americans. The richest people in the U.S. aren’t just getting several years of extra life, they’re also reaping a financial reward for their longevity - courtesy of the U.S. taxpayer. These trends will be crucial as the new administration and Congress consider any changes to Social Security, Medicare, and other programs. Even tweaks to these programs, from the retirement age to benefit formulas, could affect the rich and poor very differently.
The researchers, a group of 13 prominent economists and health policy experts 1 , tried to figure out how long Americans can expect to live based on their income, focusing on earnings in midcareer, from 41 to 51, and using Social Security data.
The results are stark. In 1980, a 50-year-old man in the wealthiest fifth of the income distribution could expect to live five years longer than a 50-year-old man in the lowest-income group. By 2010, the gap between them had jumped to 12.7 years.

In other words, the poorest fifth of 50-year-old American men can now expect to live just past 76, six months shy of the previous generation. The richest 50-year-olds should make it almost to 89, seven years longer than their parents' generation.
The study focuses on men because the researchers considered the data on women less reliable. Women's move into the workforce over the past 40 years can skew the numbers, for example, because earlier generations of women sometimes had low reported earnings while having a relatively high socioeconomic status. While the researchers weren't prepared to produce specific estimates for women, though, they were confident that women experienced a “similar if not larger change over time” compared with men, citing a previous analysis.
One important result of this 13-year life expectancy gap: Social Security and other government programs, such as Medicare, are becoming a much better deal for well-off Americans.
Three decades ago, the richest and poorest retirees could expect about the same amount of benefits out of government programs. The richest generally got larger Social Security payouts, both by qualifying for higher checks and by living longer. The poorest got more out of other programs, such as Medicaid and Social Security disability insurance. Medicare offered about the same benefits to rich and poor.
The math has shifted dramatically. As wealthier people live longer, they can expect to collect much more from Social Security over their lifetimes than the poor. This chart shows the growing gap, based on the present value of benefits to a 50-year-old looking ahead, and using 2009 U.S. dollars to account for inflation.

In 1980, a wealthier 50-year-old could expect to collect $103,000 more than a poor American. Thirty years later, the gap was $173,000. “These results suggest that Social Security is becoming significantly less progressive over time due to the widening gap in life expectancy,” the researchers write.
The U.S. retirement system looks more even-handed if you include in the analysis all government benefits received and all taxes paid by Americans after age 50. Still, longer lives are giving the rich and upper middle class a big financial boost, especially through Medicare and Social Security, even as the poorest Americans lose ground.

There are several theories on why the health of wide swaths of the U.S. is getting so much worse while the wealthy are thriving and living so much longer. Some cite rising levels of substance abuse, obesity, and suicide. Others point to the ways economic inequality drive health inequality. The cost of good health care has skyrocketed, even for people who are technically covered by insurance.
Your expected life span is obviously a factor when planning and saving for retirement. The longer you live, the more valuable Social Security is as a safety net to supplement your savings. Life expectancy trends also affect the long-term finances of entitlement programs such as Social Security.
For the moment, the most pressing question is why so many Americans are dying young, and how to stop it.
The Rich Are Living Longer and Taking More From Taxpayers