Urinalysis Notes


Color and Turbidity
clear, hazy, cloudy, amber, straw
red: blood or beets? drugs.
drugs: green, blue (Triamterene/Dyrenium = potassium-sparing diuretic used in combo w/ thiazide diuretics)

EFFECTS OF 24 HOUR STORAGE AND REFRIGERATION ON URINE CONTENTS
Leukocyte esterase: after storage ~25% of the positive samples were less reactive
Hemoglobin retests declined significantly after storage
Urine protein values increased after storage
No change in values for nitrites, glucose, and ketones.
http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/content/full/46/9/1384
Odor
normal = urinoid
"cougar pee" smell dt high dose of Coenzyme Q10 (given to cancer pts)
asparagus, curry, alcohol, coffee, turkey and onion cause distinct odors
VITAMIN C
causes false negatives in: bilirubin, glucose, hemoglobin, nitrites

BILIRUBIN
decomposes in light, false neg with vit C
high nitrates inhibits dipstick reaction
bili on dipstick is conjugated by liver
there is no unconjugated in the urine, it goes out in the feces
if bili neg and urobilinogen positive then liver is not working: hepatic or hemolytic jaundice
ddx if +: hepatocellular dz, post-hepatic obstructive jaundice
false positives: stool contamination, very high urobilinogen, pryidium color change

UROBILINOGEN
normal is neg to trace
incr in hemolytic anemia
false pos with pigments and ?
false neg: formaldehyde
GLUCOSE
spills into urine when blood glucose exceeds 160mg/dl
ddx: diabetes, renal tubular dz, Cushing's syndrome
positive dipstick finding requires confirmation: OGTT or 2 hr postprandial glucose
false neg with vit C, ketonuria, cephalosporins, pH under 5, gentisic acid (breakdown product of aspirin)
false pos: hypochlorite or peroxide contamination, phenyketones, cephalotin/keflin (1st gen cephalosporin)

KETONES
only acetone and acetoacetate are detected (beta-hydroxybutyric acid is not detected)
from fatty acid breakdown cause fruity smell
ddx: DKA, low carb diet, fasting, starvation, V/D, alcoholism, eclampsia
false pos: multistix-->highly pigmented urine or levodopa metabolites show high SG and low pH, quidel->incr phenylpyruvic acid, any pthaleins and anthraquinone derivatives in alkaline pH give red color ????
false neg: sample exposed to air (ketones volatilize)
pH
normal is 5.0-6.0 or more broadly 4.8-7.5
>7.0 is a good indicator of a UTI, or acidosis, diarrhea, high protein diet, starvation, veg eater, Cushing's
>7.0 also mbdt urea splitting bugs: pseudomonas, proteus (stone forming bug)
<4.5 mbdt diabetes, or high protein diet
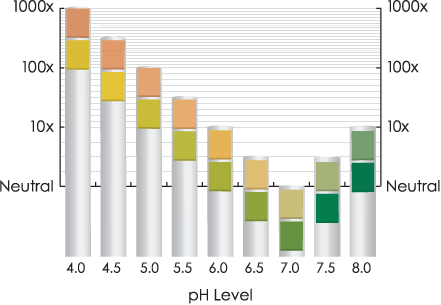
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
normal is 1.01
must be normal for an accurate pregnancy test
isosthenuria = constant SG dt renal dz, 1.0
hyposthenuria = < 1.007
hypersthenuria = > 1.025
Blood
if positive but no RBCs consider: muscle breakdown, hemolysis, bacteria, betadyne contamination
HEMOGLOBIN
false neg with vit C
ddx: UTI, CA, stones, HUS, glomerulonephritis, pyslonephirits, polycystic kidneys, intravascular hemolysis (malaria, transfusion rxn, drug rxn, severe burns, bact toxin, strenuous exercise), PNH = paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, PCH = parox cold hgbinuria
false pos: formalin, hypochlorite or peroxide contam, myoglobinuria
false neg: vit C and other non-specific O2 acceptors (uric acid, glutathione, gentisic acid)
high nitrites or high SG may delay rxn
NITRITES
neg does not rule out UTI
if suspect UTI run a culture
false neg with vit C
pos ddx if pH over 7: urea splitting bugs incl pseudomonas, proteus
ddx: metabolic or respiratory alkalosis, high veggie diet, Cushing's, some kidney stones incl triple phosphate
false pos or neg: none known
PROTEIN
normal is neg to trace, albumin is detected
ddx if +: glomerular dz, pre-eclampsia, DM, amyloidosis, strenuous exercise, stress, macroglobulinemia
false pos: if pH 9 or high, very high specific gravity
false neg: dilute urine, proteins other than albumin present (globulins, Bence-Jones, glycoproteins)
*******************************************************************************
MICROSCOPIC STUDY
10 fields at 40x
mucus threads common
urates in acid urine
phosphates in alkaline urine
*******************************************************************************
CASTS
reported by type and # per high power field (100x)
important indicators of renal dz
ddx: glomerular damage, tubular damage, inflam, infx
formed in lumen of tubules of kidney dt stasis, acidity, high solutes, abn ions/prots
usu form in distal and collecting tubules bcs urine is maximally concentrated and acid there
glue that holds them together: Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein secreted by renal tubules
casts dissolve in alkaline or neutral urine with SG under 1.003
presence of casts often accompanied by proteinuria but mb there w/o prot
types: hyaline, red, white, EC, granular (coarse and fine), waxy, fatty
mb hard to distinguish dt age, or be mixed
degeneration-->granular appearance? a theory
HYALINE CASTS
most common, early epithelial casts, seen in the mildest renal dz of any kind
mb found in normal urine, more after exercise or dehydration
made of gelled Tamm-Horsfall protein plus any inclusions
low refractive index, view under low light
colorless, homogenous, transparent, rounded ends
almost invisible under microscope, wispy




WHITE CELL CASTS
mostly PMNs
ddx: renal infarct, infx, noninfx inflam, acute/interstitial/lupus nephritis, glomerular dz
when cells degenerate-->granular appearance



RED CELL CASTS
means renal hematuria, always pathologic
usu dx glomerular dz: acute glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, Goodpastures, SBE, renal trauma
renal infarction, severe pyelonephritis, RCHF, renal vein thrombosis, periarteritis nodosa
may appear brown or colorless
may contain only a few RBC's in a prot matrix or be solid packed RBCs
RBCs are smaller than ECs
RBC casts can degenerate to hemoglobin or blood cast, brown-red in color
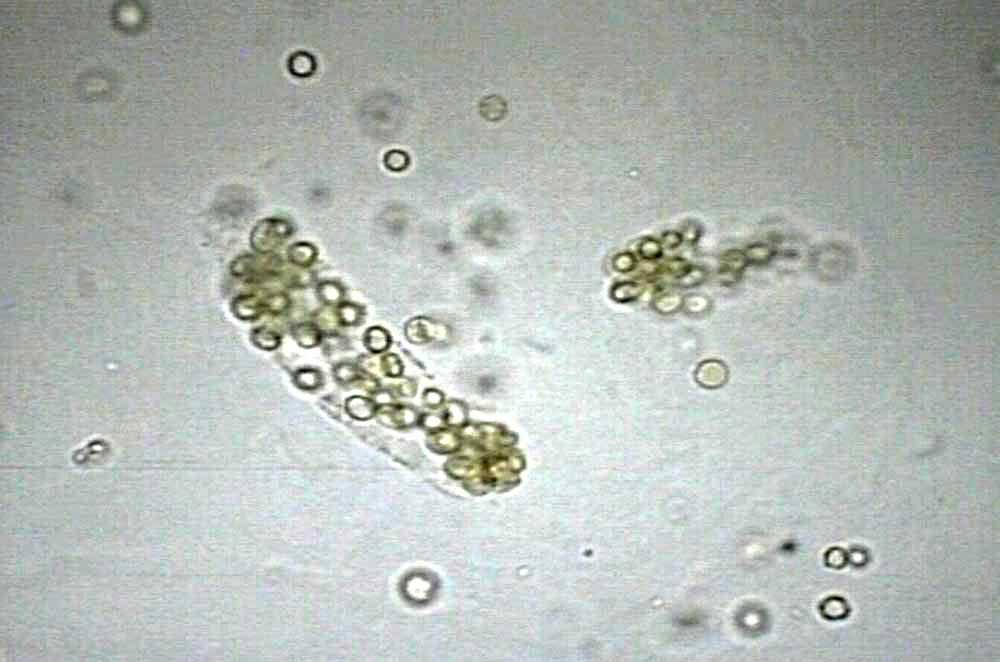
BROAD CASTS
aka "renal failure casts"
2-6x wider than ordinary casts
formed in pathologically dilated/atrophied or in collecting tubules


GRANULAR CASTS
mbdt degen of cellular cast or dt direct agg of serum prots into matrix of Tamm-Horsfall
initially large and coarse
when prolonged urine staiss break down to fine granules
usu indic sig renal dz
mb present for short time following strenuous exercise
coarse vs fine doesn't matter much but coarse may look black while fine mb pale or yellow

EPITHELIAL CELL CASTS
dt stasis and desquamation of renal tubular ECs
rarely seen bcs renal dz rarely affects tubules (necrosis)
mb in urine after nephrotoxin exposure or virusis (CMV, HSV)
mb present in severe chronic renal dz and rejection of kidney allograft
ECs mb in parallel rows or haphazard, if irreg mb from diff parts of tubule
ECs vary in size, shape, stage of degen



WAXY CASTS
high refractive index, yellow, gray or colorless
smooth homogenous appearance
serum proteins are present in homogenous distribution
may occur as short broad casts with blunt or broken ends, crack or serrated edges
mb formed of degenerated granular casts
ddx: severe chronic renal filuare, malignant HTN, renal amyloidosis, diabetic nephropathy
ddx: acute renal dz, tubular inflam/degen, transplant rejection


FATTY CASTS
incorporated free fat droplets or oval fat bodies
if fat is chol, drops will be anisotropic: under polarized light will show "maltese cross"
isotropic = TGs that will not polarize but will stain with Sudan III or Oil Red O
ddx: fatty degen of tubulrr epithelium, nephrotic syndrome, diabetic glomeruloscleorisis, lipoid nephrosis, chornic glomerulonephritis, Kimmelstiel Wilson syndrome, lupus, toxic renal poisoning

FAT BODIES
usu seen in conjunction w/ heavy proteinuria
fat bodies in cells
http://www.agora.crosemont.qc.ca/urinesediments/doceng/doc_015.html
Oval fat bodies are cells with birefringent fat droplets within their cytoplasm
birefringence = resolution or splitting of a light wave into two unequally reflected or transmitted waves by an optically anisotropic medium
under low power magnification ofb's seen as lg brown spots
color dt pigmented fat
true oval fat bodies show "maltese cross" interference pattern under polarized light
cross pattern dt esterified cholesterol in a liquid crystal state
FAT DROPLETS
fat droplets are free
may originate from a vacuolar fatty degeneration of intracytoplasmic membranes
frequent
cells kept for several days in a urine develop all kinds of vacuoles
sometimes droplets sim to those in the oval fat bodies, except for the birefringence
intracytoplasmic droplets can also originate from phagocyted & digested material
can stain w/ Sudan, Fat Red 7B, and fat stains
"to our view, staining is of little use", "birefringent criteria is easy to observe"
some fat droplets lose their birefringent characteristics
sometimes possible to correct the crystalline disorganization
by gently heating the slide, followed by a rapid cooling
nature of oval fat bodies is debated
Schumann: oval renal proximal tubular cell with a fat droplets filled cytoplasm
Stamey: oval fat bodies are in fact macrophages also known as foam cells
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
Oval fat bodies in a high proteinuria context assoc w/ nephrotic syndrome link between the nephrotic syndrome and lipiduria not known
Lipiduria seems to be related to the proteinuria, and not to plasmatic lipids level
??? mbdt a specific apolipoprotein accessing, like the albumin, to the urinary space through the glomerule. Filtrated free fatty acid adsorbed to the urinary albumin could play a role in the intracytoplasmic accumulation of fat by the renal proximal tubular cell. (Oval fat bodies are often seen with the droplets filling one side of the cell)
Oval fat bodies are not specific to the nephrotic syndrome. These cells are sometime seen in specimens with a normal proteinuria. This situation can be explained by the presence of fatty macrophages often seen in chronic inflammation sites.
Stamey reports oval fat macrophages in seminal fluid of pts w/ prostatitis
Foam cells can be seen in many human fluids: bile, bronchial...
********************************************************************************
CRYSTALS
Clinically significant (pathological) crystals:
Cysteine, Tyrosine,
Ammonium biurate (abn in fresh urine), Leucine (maple syrup urine dz)
urates-->acid urine
phosphates-->alkaline urine
CYSTEINE
six sided
congenital


TYROSINE
swishy lines mb parallel or from a midpoint
liver, leukemia, typhoid, smallpox

AMMONIUM BIURATE
the blobby ones
abn in fresh urine only

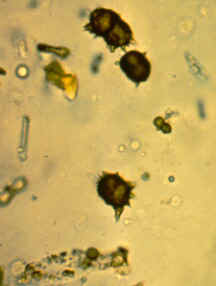
LEUCINE
little spot with circle or dot or dots inside


why does this leucine look like hot cross bun/starch?

URIC ACID CRYSTALS
sort of six sided but corners are round and a bit oblong
like a football

CALCIUM OXALATE
colorless, square or rectangular with X shaped crosshatching
from vit C breakdown
size varies but usu small


SODIUM URATES
acid urine
needle shaped with blunt end
may form florette
usu small


HIPPURIC ACID
six sided with two long sides
rare


CALCIUM CARBONATE
little dumbells


AMORPHOUS PHOSPHATES
little spots in alkaline or neutral urine

AMORPHOUS SEDIMENT
when you don't know what to call it
colorless, pink-orange, red-brown
granules with no obvious shape
more dense/opaque than bacteria
CALCIUM PHOSPHATES
needles and spikes and sometimes florettes
looks like sodium urates but is in alkaline urine


TRIPLE PHOSPHATES
prism with oblique ends, glassy appearance
size variable, some mb very large
alkaline or neutral urine
edges may show to look like folds of envelope
or like a dory hull in some positions


STARCH
hot cross buns



SULFA
(renal drug)
bow ties or ginkgo leaves


CHOLESTEROL
trapezoids, long or squat


CRYSTAL QUIZ: WHAT ARE THESE?

A KIDNEY IN ACUTE RENAL FAILURE

ANOTHER SITE FOR URINE SEDIMENT REVIEW
http://www.enjoypath.com/cp/Chem/Urine-Morphology/Urine-morphology.htm
ANSWERS TO QUIZ (my best guess, and I bet you a dollar this slide will be on the exam!!!)
top left: calcium oxalate
top right: triple phosphate
bottom left: uric acid
bottom right: cysteine
GREAT RESOURCE FOR THE LAY PERSON
http://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2013/05/30/urine.aspx