Jurassic Period
Pangaea: The Movement of the Plates-
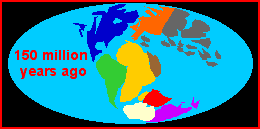
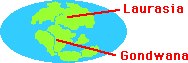
The Jurassic saw disintegration of Pangea that began in the Triassic continuing apace. The supercontinent begins to rotate, but the different components of the huge mass rotated at different rates and then in different directions, causeing rift valleys. Pangea was classified in to two parts Laurasia and Gondwana.
This was North America drifting westward, opening the Gulf of Mexico, forming the central Atlantic. As Greenland-North America separate from Europe-Africa and slide over the Pacific Ocean floor, mountain-building events are triggered that created the North American Cordillera (the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada). A huge arc was built on western North America and the Nevadan orogeny begins. Cimmeria begins its collision with Laurasia to form the Cimmerian orogeny.
In Gondwana the initial narrow split between South America and Africa that began during the Triassic widened into a configuration resembling the present-day Red Sea. New sea floor formed along the nascent South Atlantic. This lengthened into a long, narrow seaway between South America and Africa. The Western side South America was subducted by an opposing oceanic plate. A great rift separates Antarctica from the southern ends of South America and Africa, developing an arm that extends eastward from South Africa along what is presently the eastern side of India, which began drifting northward.. Volcanoes located along these rifts erupted and issued huge amounts of basaltic lavas. The separated segments of Gondwanaland move slowly northward, turning gently counter-clockwise. Early rifting along the Australia-Antarctica join provided moist forested conditions that became coal deposits.