Scalp and Face
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
SCALP AND FACE
I. Definition/ Extension
Extent of Scalp:
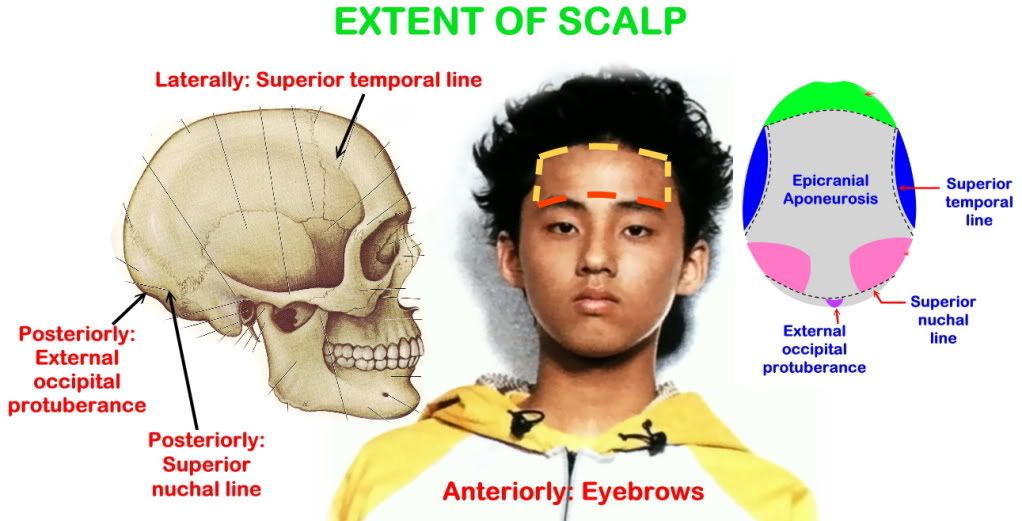
Anteriorly: Eyebrow
Posteriorly: Superior nuchal line and external occipital protuberance
Laterally: Superior temporal lines
Inferiorly: Zygomatic arch
Layer of Scalp
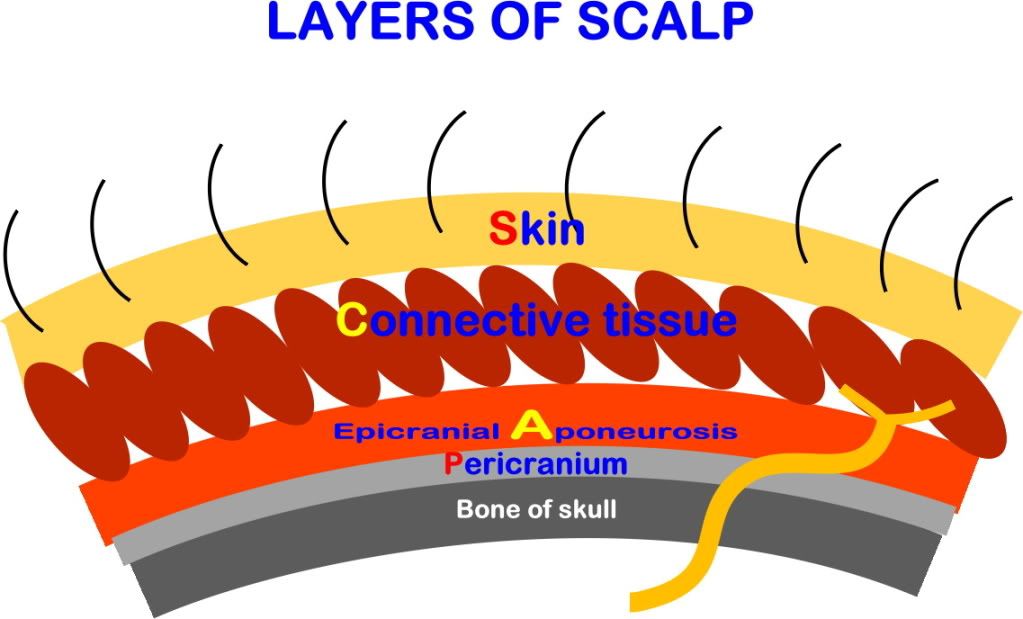
S: Skin - Rich in hair and sebaceous glands
C: Connective tissue of superficial fascia - Contains blood vessels and nerves
A: Epicranial aponeurosis - Strong sheet of fibrous tissue connected to:
x Anteriorly: Frontalis muscle
x Posteriorly: Occipitalis muscle
x Laterally: Superior temporal lines
L: Loose areolar tissue - Allow free movement of layer of scalp on skull
- Contain emissary veins (Dangerous area of scalp) and small arteries
- Extend downward to eyelids so bleeding inside it leads to black eye
P: Pericranium - Periosteum of skull
FACE
Definition/ Extension of Face:
Part of head which extend from eyebrows superiorly to chin inferiorly and between ears laterally.
II. Muscles
Muscle of Scalp: Occipitofrontalis Muscle
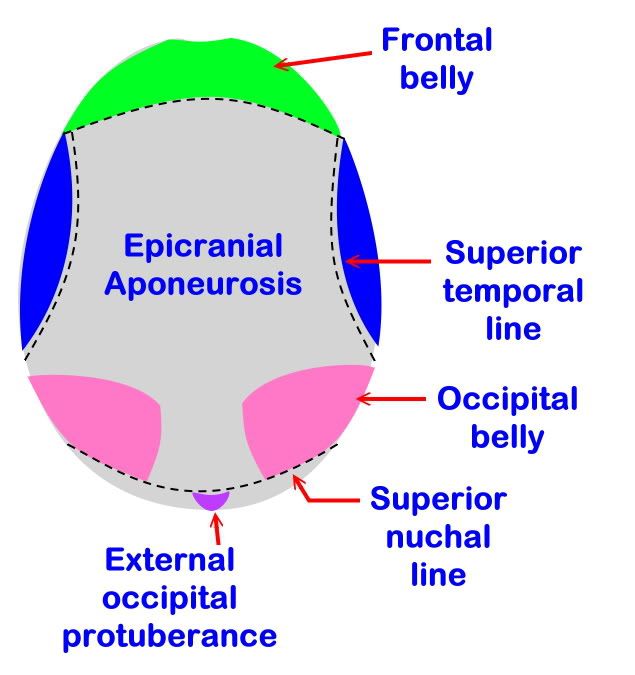
Formed of two frontal bellies and two occipital bellies
1. Frontalis (Frontal belly)
- Origin: Skin of eyebrows and forehead
- Insertion: Epicranial aponeurosis
- Nerve supply: Temporal branch of facial nerve (CVII)
- Action: Raise eyebrows and wrinkles skin of forehead
2. Occipitalis (Occipital belly)
- Origin: Highest nuchal line
- Insertion: Epicranial aponeurosis
- Nerve supply: Posterior auricular branch of facial nerve (CVII)
- Action: Move scalp backward
Muscles of Face
1. Protect organs (Eyes, mouth, nose, ears)
2. Called muscles of expression
3. Surround facial openings and act as sphincters and dilators of them
4. Develop from same embryonical origin; 2nd pharyngeal arch
5. Have bony origin and cutaneous insertion
6. Supplied by facial nerve
A. Orbicularis Oculi Muscle
1. Orbital part
Origin:
1. Medial palpebral ligament
2. Frontal process of maxilla
3. Maxillary process of frontal
Insertion:
- Fibres radiate around margins of orbital cavities and partially inserted into skin
- Same as origin but from bone into skin
Action:
- Close eyelid forcibly for protection
2. Palpebral part
Origin:
1. Medial palpebral ligament
2. Frontal process of maxilla
3. Maxillary process of frontal bone
Insertion:
- Forming ring in substance of eyelid to be inserted into
1. Skin
2. Tarsal plate
3. Lateral palpebral ligament
Action:
- Close eyelid gently as in sleep
3. Lacrimal part
Origin: From lacrimal crest and lacrimal sac
Insertion: Tarsal plate of upper and lower eyelids
Action: Regulates size of lacrimal sac (Help in drainage of tears)
Nerve supply: The whole muscle is supplied by temporal and zygomatic branches of facial nerve
Branches of Facial Nerve:
1. Temporal
2. Zygomatic
3. Buccal
4. Mandible
5. Cervical
B. Buccinators Muscle
Origin:
1. Upper fibres: From alveolar margin of maxilla opposite molar teeth
2. Middle fibres: From pterygo-mandibular ligament
3. Lower fibres: From alveolar margin of mandible opposite molar teeth
Insertion:
1. Upper fibres: Pass straight to upper lip
2. Middle fibres: Decussate at modulus so upper fibres pass into lower lip and lower fibres into upper lip
3. Lower fibres: Pass straight to lower lip
Nerve Supply: Buccal branch of facial nerve
Action:
1. Compresses cheek against gums and teeth during blowing
2. Prevents accumulation of food in vestibule of mouth
Relations:
a. Deep
1. Buccal mucosa (Mucous membrane of cheek)
2. Pharyngeo-basilar fascia
b. Superficial
1. Buccal pad of fat
2. Parotid duct (Pierces it opposite upper 2nd molar tooth)
3. Nerves: Buccal branch of facial (Motor) and buccal branch of mandibular (Sensory)
4. Vessels: Facial artery and vein, deep facial vein and buccal artery
5. Muscles: Zygomaticus major and minor
C. Orbicularis Oris Muscle
Formation:
1. Extrinsic fibres: From muscle around mouth and inserted into deep surface of skin and mucous membrane of lips
2. Intrinsic fibres: from mucous membrane to skin between extrinsic fibre
Nerve Supply: Buccal and mandibular branches of facial nerve
Action:
1. Sphincter of mouth opening (Compresses lips against teeth)
2. Articulation of letters during speech
III. Arterial Supply
Arterial Supply of Scalp

A. In front of auricle
Common carotid artery (Originate from left side arch of aorta and right side brachiocephalic artery) gives two branches; internal carotid and external carotid.
External carotid is out of cranial cavity and gives branches in neck.
Branches of external carotid artery are superficial temporal artery, posterior auricular artery and occipital artery supplying around scalp.
Internal carotid enters cranial cavity and pass out from orbital cavity.
Branches of internal carotid artery are supratrochlear and supraorbital arteries supplying scalp.
1. Supratrochlear
2. Supraorbital
Origin: Both are branches from ophthalmic branch of internal carotid artery
Course: Pass out from orbital cavity with the corresponding nerves to forehead and scalp
Distribution: Supply anterior part of scalp
3. Superficial temporal artery

Origin: Smaller of two branches of external carotid artery which in parotid gland
Course: Appears at upper border of parotid gland in front of auricle
Accompanied by superficial temporal vein and auriculotemporal nerve
Termination: Dividing into 2 branches; anterior and posterior
Branches:
1. Transverse facial artery - Passes transversely between parotid duct and zygomatic arch, supplies lateral part of face
2. Anterior auricular arteries - Supply auricle and external auditory meatus
3. Zygomatico-orbital artery - Supplies face
4. Middle temporal artery - Runs deep to temporalis muscle to supply temporal fossa
5. Anterior terminal artery - Runs forwards towards frontal eminence to supply anterior part of temple
6. Posterior terminal artery - Runs backwards towards parietal eminence to supply posterior part of temple

B. Behind ear
1. Posterior auricular artery
- Branch from external carotid artery
- Supplies scalp behind ear
2. Occipital artery
- Branch from external carotid artery
- Supplies back of scalp

1. Facial Artery
Origin: Branch of external carotid artery
Course:
- Enters face by passing over lower border of mandible in front of masseter muscle
- Runs upwards and forwards in a tortuous course towards side of nose to a point ½ inch lateral to angle of mouth
Termination: At medial angle of eye by anastomosing with ophthalmic artery
Branches in Face:
a. Inferior Labial artery: To lower lip
b. Superior Labial artery: To upper lip
c. Lateral nasal artery: To lateral side of nose
d. Angular artery: At medial angle of eye
e. Muscular arteries: To surrounding muscles
2. Transverse Facial Artery
Origin: From superficial temporal inside parotid gland
Course:
- Passes transversally from anterior border of parotid gland between parotid duct and zygomatic arch to supply lateral part of face
3. Superficial Temporal Artery
Origin: Smaller of two branches of external carotid artery which in parotid gland
Course: Appears at upper border of parotid gland in front of auricle
Accompanied by superficial temporal vein and auriculotemporal nerve
Termination: Dividing into 2 branches; anterior and posterior
Branches:
a) Transverse facial artery - Passes transversely between parotid duct and zygomatic arch, supplies lateral part of face
b) Anterior auricular arteries - Supply auricle and external auditory meatus
c) Zygomatico-orbital artery - Supplies face
d) Middle temporal artery - Runs deep to temporalis muscle to supply temporal fossa
e) Anterior terminal artery - Runs forwards towards frontal eminence to supply anterior part of temple
f) Posterior terminal artery - Runs backwards towards parietal eminence to supply posterior part of temple
4. Arteries accompanying cutaneous branches of trigeminal nerve
a. Supratrochlear, supraorbital, infratrochlear and lacrimal arteries
o Terminal branches of ophthalmic artery from internal carotid
o Supply upper part of face
b. Infraorbital artery and buccal arteries
o Branches of maxillary artery
o Supply middle part of face
c. Mental artery
o Branch of inferior alveolar artery of maxillary artery
o Supplies lower lip and chin
IV. Venous Drainage
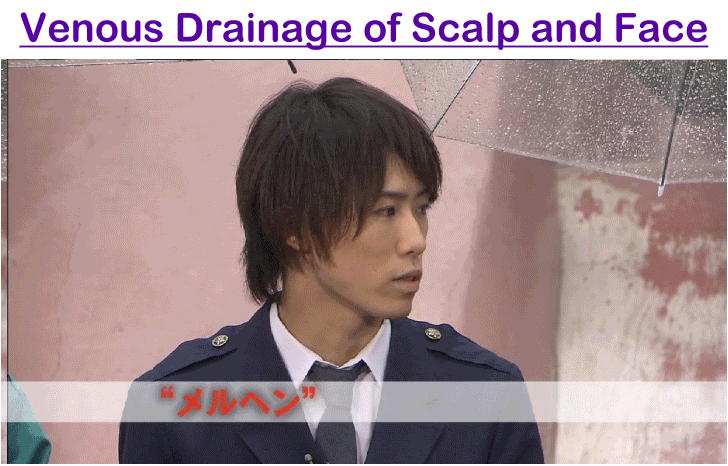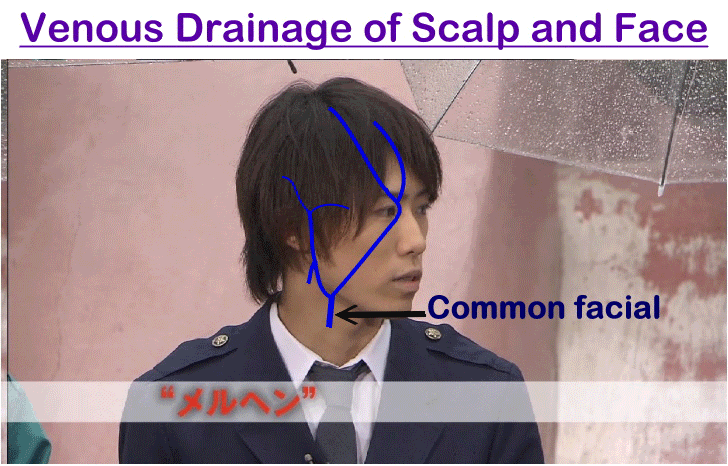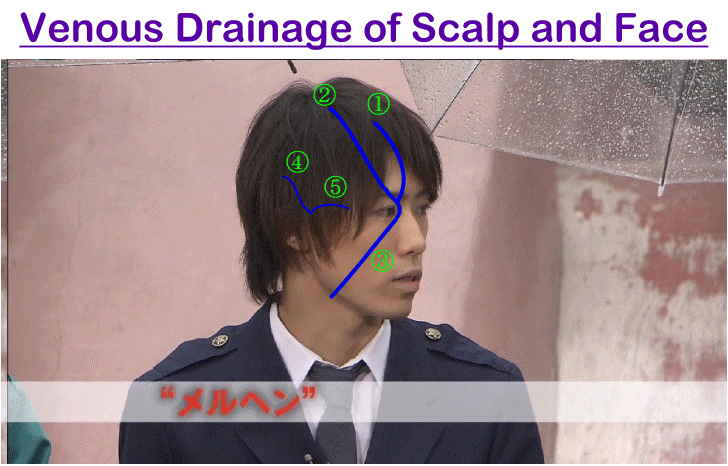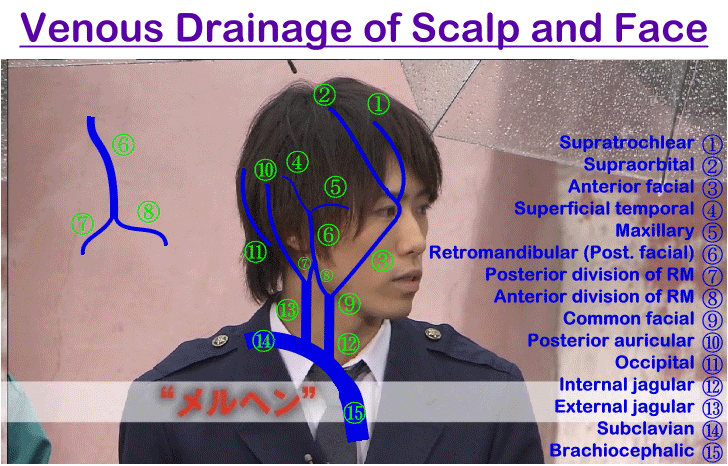
Venous Drainage of Scalp
A. Superficial Veins
(1) Supratrochlear vein and (2) supraorbital vein unite together at inner angle of orbit to form anterior facial vein
(3) Superficial temporal vein descends in front of auricle to enter parotid gland where it unites with maxillary vein forming posterior facial (Retromandibular) vein
(4) Posterior auricular vein descends behind auricle, unites with posterior division of retromandibular vein forming external jagular vein
(5) Occipital vein accompanies occipital artery to drain into occipital venous plexus
B. Deep Veins
- Emissary veins in subaponeurotic space which communicate with cerebral venous sinuses
Venous Drainage of Face
1. Anterior Facial Vein
Begin: Medial angle of eye by union of supraorbital, supratrochlear and angular veins
Course: Run downwards between nose and cheek behind facial artery
Termination: Join in neck by anterior branch of posterior facial vein forming common facial vein
Tributaries: Veins from side of nose and lips
Communication: Communicated to cavernous sinus by
a) With superior ophthalmic veins at medial angle of eye
b) With pterygoid plexus of veins through deep facial vein
2. Posterior Facial (Retromandibular) Vein
Begin: Upper part of parotid gland by union of maxillary and superficial temporal veins
Course: Run through substance of parotid gland
Termination: Divides into 2 parts
a) Anterior division - Joins with anterior facial vein forming common facial vein which terminate into internal jagular vein
b) Posterior division - Joins with posterior auricular vein forming external jagular vein
3. Superficial Temporal Vein
- Descends in front of auricle to enter parotid gland
- Unites with maxillary vein forming posterior facial (Retromandibular) vein
V. Lymph Drainage
Lymph Drainage of Scalp

1. Anterior part of scalp and face - Drains into submandibular lymph nodes
2. Lateral part of scalp - Drains into preauricular (Parotid) lymph nodes
3. Posterior part of scalp - Drains into mastoid and occipital lymph nodes
Lymph Drainage of Face

1. Upper part: Includes great part of forehead. Lateral ½ of eyelids, cheeks and parotid region drain into preauricular (Parotid) lymph nodes
2. Lower part: Includes central part of lower lip and chin drain into submental lymph nodes
3. Middle part: Rest of face drain into submandibular lymph nodes
4. All the groups finally drain into deep cervical lymph nodes
VI. Sensory Nerve Supply

Nerve Supply of Scalp
10 nerves on each side:
5 nerves in front of auricle; 4 sensory (Branches of trigeminal nerve) and 1 motor (Branch of facial nerve)
5 nerves behind auricle; 4 sensory (Branches of cervical nerves) and 1 motor (Branch of facial nerve)
i. SENSORY TO SCALP
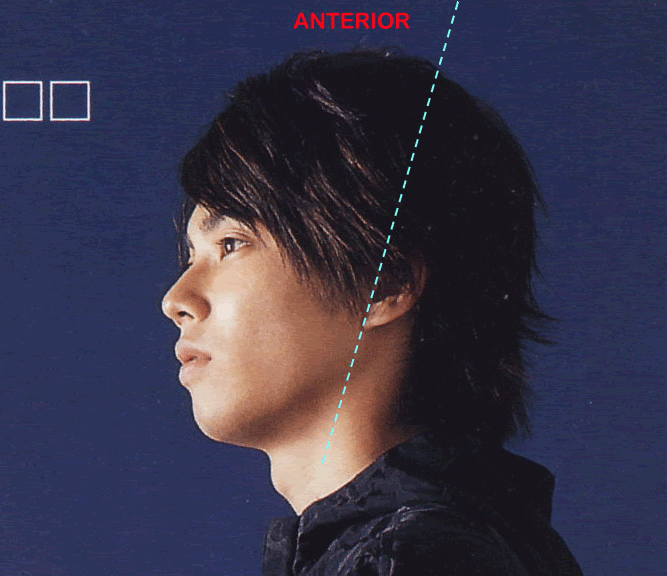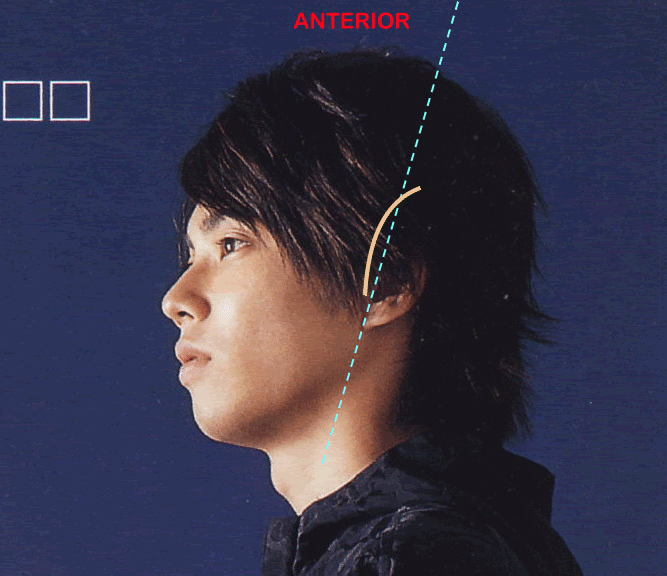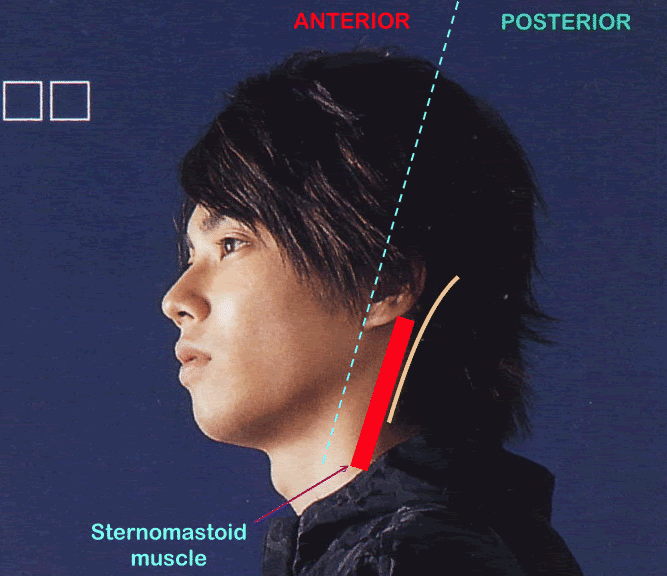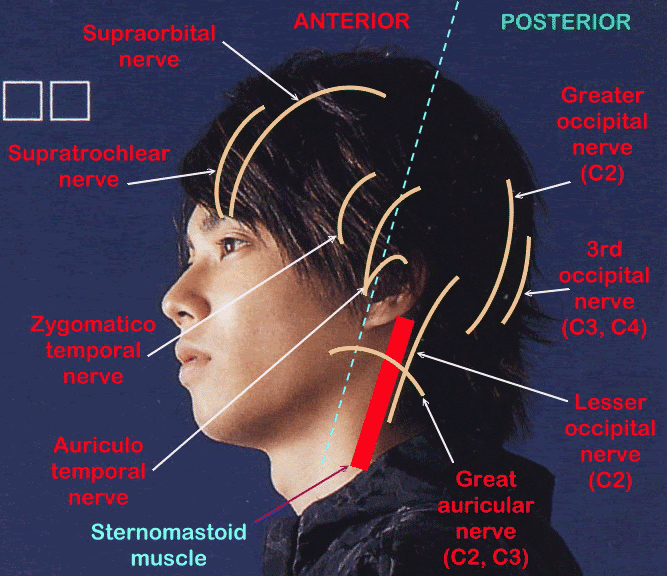
A. In front of auricle
1. Supraorbital nerve
- Branch of frontal nerve from ophthalmic nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out of orbit through supraorbital foramen
- Supplies forehead and scalp till vertex
2. Supratrochlear nerve
- Branch of frontal nerve from ophthalmic nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Appear above trochlear of superior oblique muscle, 1 inch from midline
- Supplies medial part of upper eyelid, middle of forehead and scalp near midline
3. Zygomaticotemporal nerve
- Branch of zygomatic nerve of maxillaru nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out from zygomaticotemporal foramen
- Supplies anterior part of temple opposite pterion
4. Auriculotemporal nerve
- Branch of posterior division of mandibular nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Appears at upper border of parotid gland and runs in front of auricle
- Supplies posterior part of temple
B. Behind ear
1. Great auricular nerve
- Branch of cervical plexus (Ventral C2 and C3)
- Supply
(a) Area below auricle
(b) Ext6ernal auditory meatus
(c) Opposite angle of mandible
2. Lesser occipital nerve
- Branch of cervical plexus (Ventral C2)
- Supplies back of auricle and area behind it
3. Greater occipital nerve
- Branch of cervical plexus (Dorsal C2)
- Pierces trapezius, 1 inch lateral to external occipital protuberance
- Supplies skin of back of scalp lateral to external occipital protuberance
4. Third occipital nerve
- Branch of cervical plexus (Dorsal C3)
- Pierces trapeius, lies close to external occipital protuberance
- Supplies upper part of neck below external occipital protuberance
i. SENSORY TO FACE
- Supplied by trigeminal nerve except
o Area of skin overlaying angle of mandible by great auricular nerve of cervical plexus
- Cutaneous branches of trigeminal nerve are:
o 5 from ophthalmic
o 3 from maxillary
o 3 from mandibular
A. Ophthalmic Branches
1. Supraorbital nerve
- Branch of frontal nerve from ophthalmic nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out of orbit through supraorbital foramen
- Supplies forehead and scalp till vertex
2. Supratrochlear nerve
- Branch of frontal nerve from ophthalmic nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Appear above trochlear of superior oblique muscle, 1 inch from midline
- Supplies medial part of upper eyelid, middle of forehead and scalp near midline
3. Palpebral nerve
- Branch from lacrimal nerve of ophthalmic nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out of orbit through its superiolateral part
- Supplies lateral part of upper eyelid
4. Infratrochlear
- Branch from nasociliary of ophthalmic nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out of orbit below trochlear of superior oblique muscle
- Supplies medial part of lower eyelid
5. External nasal nerve
- Branch from nasociliary of ophthalmic nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out between nasal bone and upper nasal cartilage
- Supplies lower part of nose
B. Maxillary Branches
1. Infraorbital nerve
- Continuation of maxillary nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out through infraorbital foramen
- Give 3 terminal branches:
a) Palpebral: Supply conjunctiva and skin of lateral part of lower eyelid
b) Nasal: Supply ala of nose
c) Labial: Supply skin and mucous membrane of upper lip
2. Zygomatico-facial nerve
- Branch from zygomatic nerve of maxillary nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out through zygomatico-facial foramen
- Supply overlaying skin (Cheek)
3. Zygomatico-temporal nerve
- Branch of zygomatic nerve of maxillary nerve of trigeminal nerve
- Comes out through zygomatico-temporal foramen
- Supply overlying skin (Anterior part of temple)
C. Mandibular Branches
1. Mental nerve
- Comes out from mental foramen in body of mandible
- Supply lower lip and chin
2. Buccal nerve
- Comes out by passing between masseter and buccinator muscles
- Supplies skin and mucous membrane of cheek
3. Auriculo-temporal nerve
- Passes upwards in front of auricle
- Supplies:
a) Auricular branch: Anterior part of ear and tragus
b) Temporal branch: Posterior part of temple
VII. Motor Nerve Supply

MOTOR SUPPLY OF SCALP
a) In front of auricle: Temporal branch of facial nerve
- Branch of facial nerve
- Supplies (a) Frontalis muscle
(b) Upper part of orbicularis oculi
(c) Auricularis anterior and posterior
b) Behind ear: Posterior auricular nerve
- Branch of facial nerve
- Supplies occipitalis and auricularis posterior muscles
ii. MOTOR SUPPLY OF FACE
• Facial nerve
- Motor nerve of face
- Comes out at base of skull through stylomastoid foramen
- Runs forwards to enter posterior surface of parotid gland
- Divides into 5 terminal branches:
o Temporal branch
o Zygomatic branch
o Buccal branch (Superior and inferior)
o Mandibular branch
o Cervical branch
Correct me for any mistakes