Волны на свободной поверхности жидкости
Волны на свободной поверхности жидкости
(случай глубокой воды)
Материалы к школьному занятию.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stokes_wave

Stokes waves of maximum wave height on deep water, under the action of gravity.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_wave
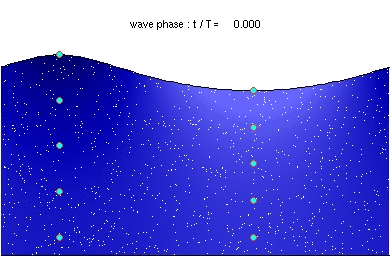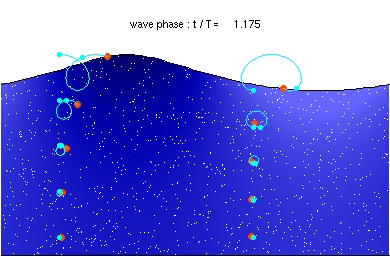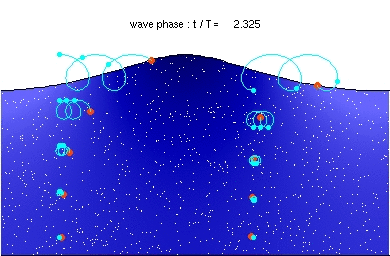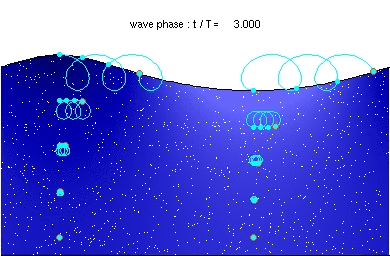
Water particle motion of a deep water wave
Stokes drift in deep water waves, with a wave length of about twice the water depth. The ratio of wave height to wavelength is H/λ=0.092.
Description of the animation: The red circles are the present positions of massless particles, moving with the flow velocity. The light-blue line gives the path of these particles, and the light-blue circles the particle position after each wave period. The white dots are fluid particles, also followed in time. In the case shown here, the mean Eulerian horizontal velocity below the wave trough is zero. Observe that the wave period, experienced by a fluid particle near the free surface, is different from the wave period at a fixed horizontal position (as indicated by the light-blue circles). This is due to the Doppler shift.
The wave physics are computed with the Rienecker & Fenton (R&F) streamfunction theory; for a computer code to compute these see: J.D. Fenton (1988) "The numerical solution of steady water wave problems". Computers & Geosciences 14(3), pp. 357-368. The animations are made from the R&F results with a series of Matlab scripts and batch files.

Рекомендется к прочтению.
Прандтль Л. Гидроаэромеханика. - Ижевск: НИЦ «Регулярная и хаотическая динамика», 2000, - 576 с.
Нас будут интересовать стр 128 - 129 начало параграфа 15. Вот все это on-line: http://scask.ru/d_book_gam.php?id=27
На всякий случай скопирую все в журнал, и добавлю несколько последующих страниц.









Дополнительные материалы - Курсовая работа https://works.doklad.ru/view/b6Ner-f7tf8/all.html
(случай глубокой воды)
Материалы к школьному занятию.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stokes_wave

Stokes waves of maximum wave height on deep water, under the action of gravity.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_wave

Water particle motion of a deep water wave
Stokes drift in deep water waves, with a wave length of about twice the water depth. The ratio of wave height to wavelength is H/λ=0.092.
Description of the animation: The red circles are the present positions of massless particles, moving with the flow velocity. The light-blue line gives the path of these particles, and the light-blue circles the particle position after each wave period. The white dots are fluid particles, also followed in time. In the case shown here, the mean Eulerian horizontal velocity below the wave trough is zero. Observe that the wave period, experienced by a fluid particle near the free surface, is different from the wave period at a fixed horizontal position (as indicated by the light-blue circles). This is due to the Doppler shift.
The wave physics are computed with the Rienecker & Fenton (R&F) streamfunction theory; for a computer code to compute these see: J.D. Fenton (1988) "The numerical solution of steady water wave problems". Computers & Geosciences 14(3), pp. 357-368. The animations are made from the R&F results with a series of Matlab scripts and batch files.

Рекомендется к прочтению.
Прандтль Л. Гидроаэромеханика. - Ижевск: НИЦ «Регулярная и хаотическая динамика», 2000, - 576 с.
Нас будут интересовать стр 128 - 129 начало параграфа 15. Вот все это on-line: http://scask.ru/d_book_gam.php?id=27
На всякий случай скопирую все в журнал, и добавлю несколько последующих страниц.









Дополнительные материалы - Курсовая работа https://works.doklad.ru/view/b6Ner-f7tf8/all.html